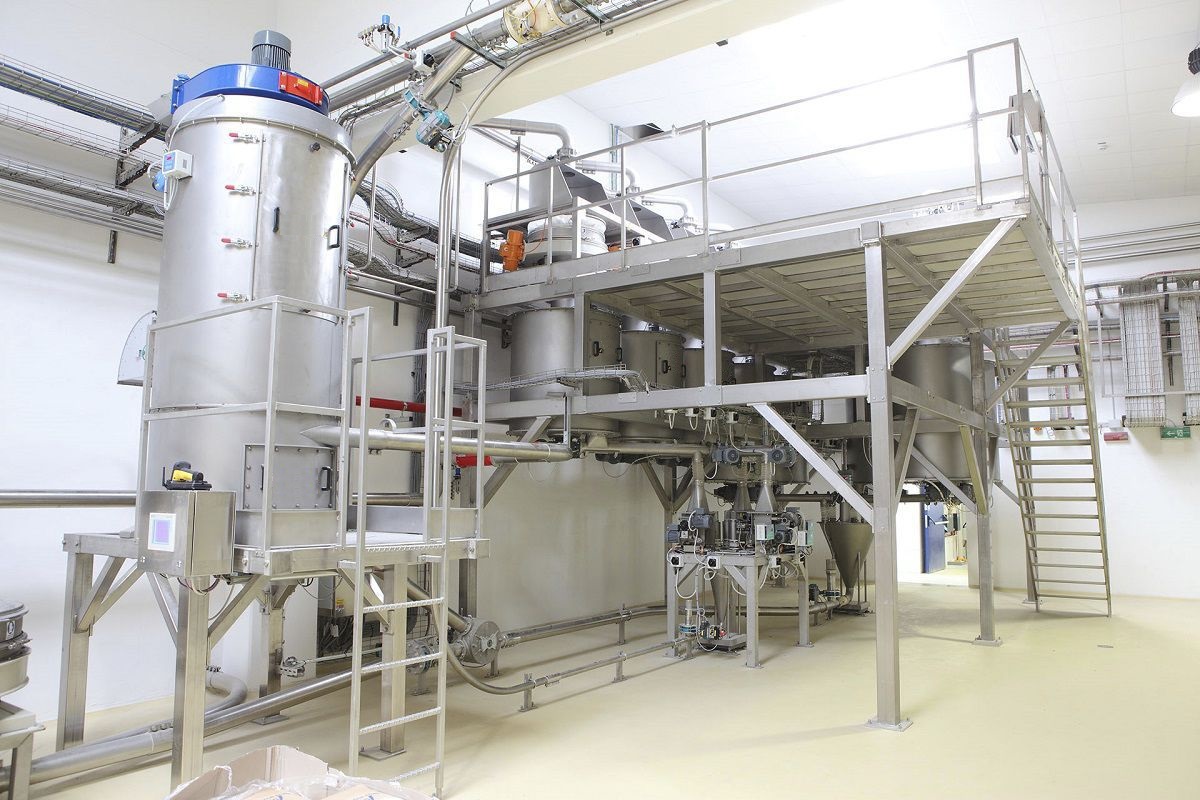
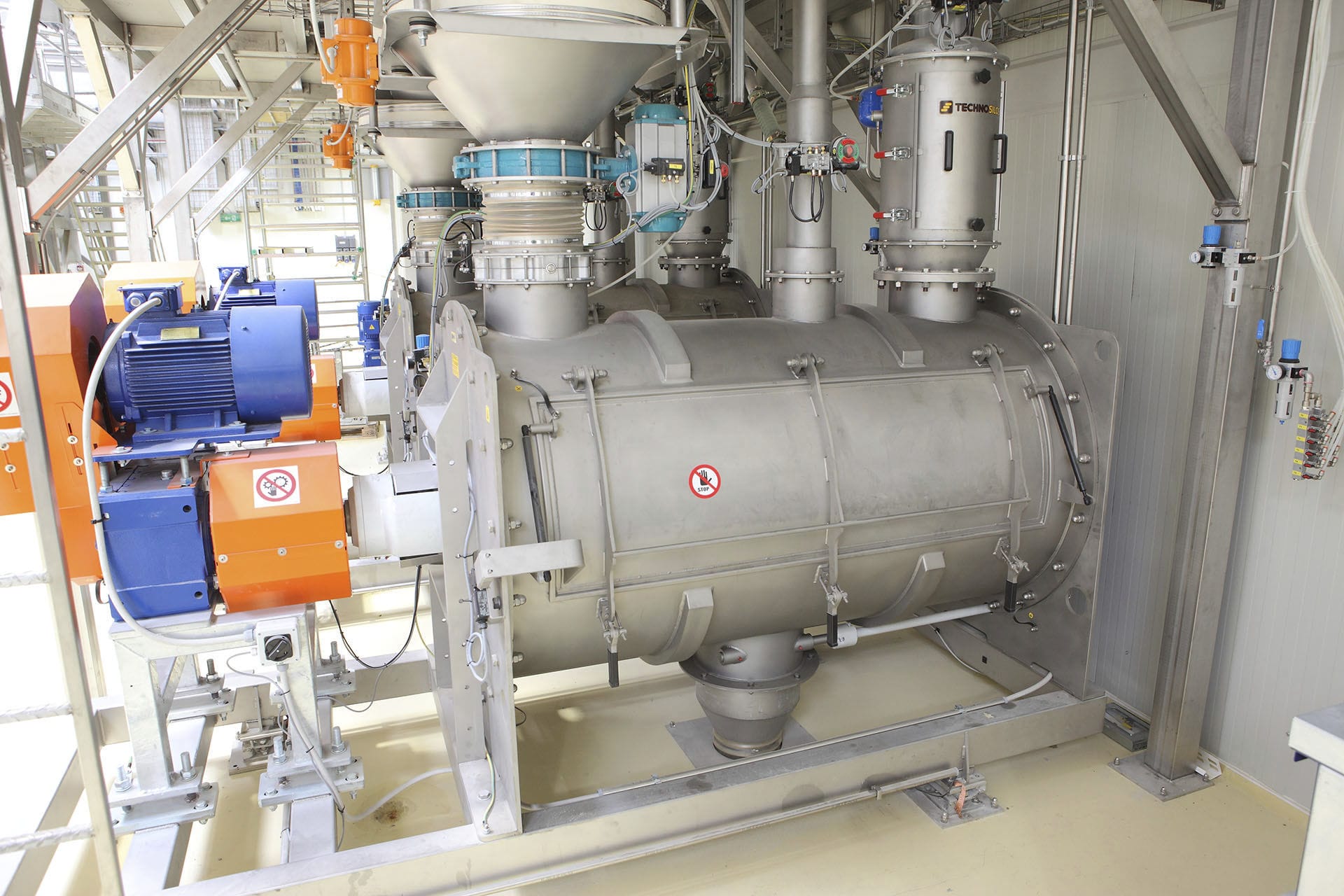
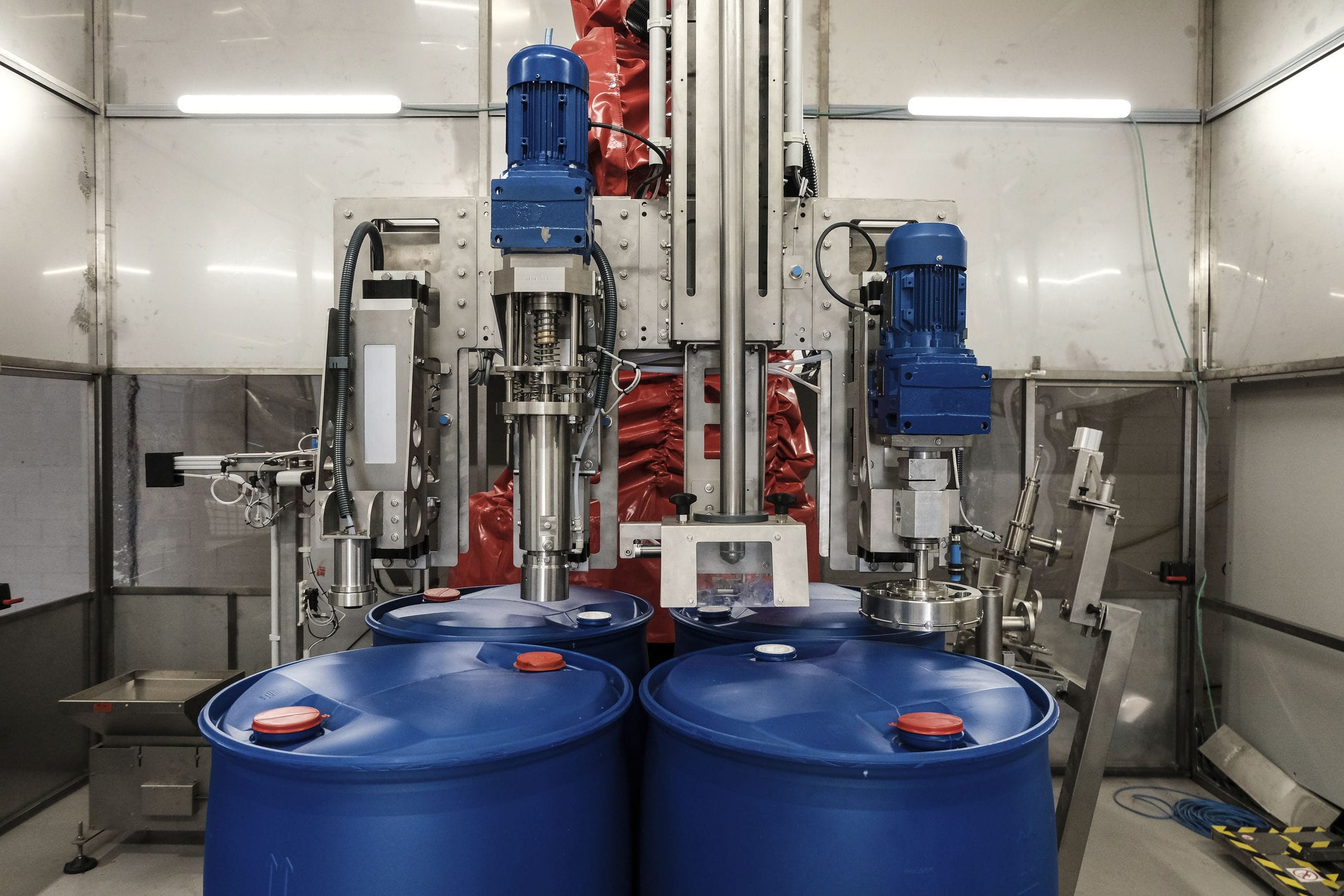
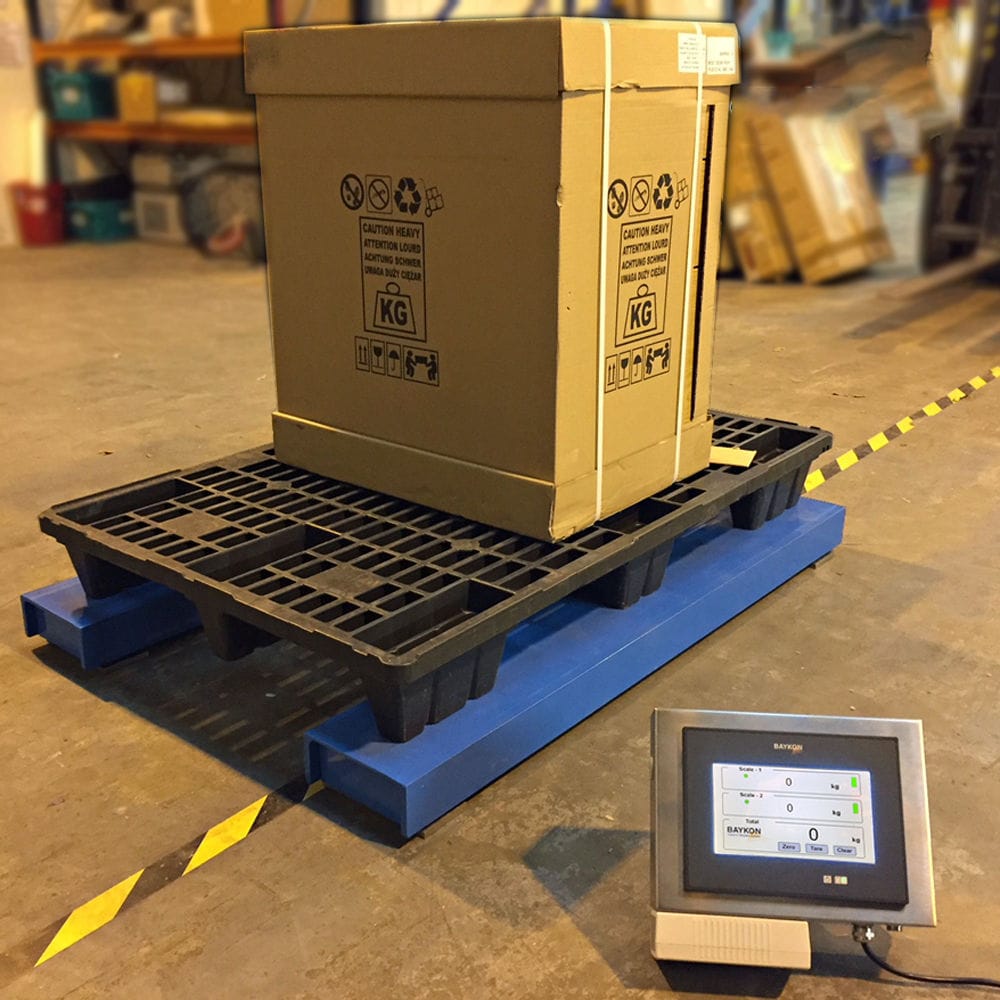
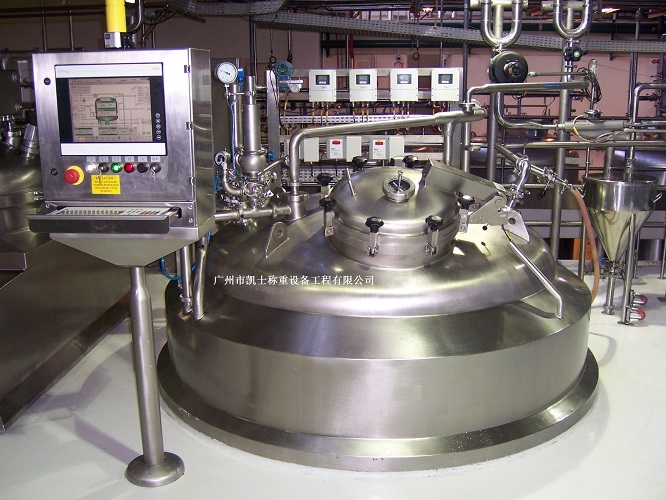
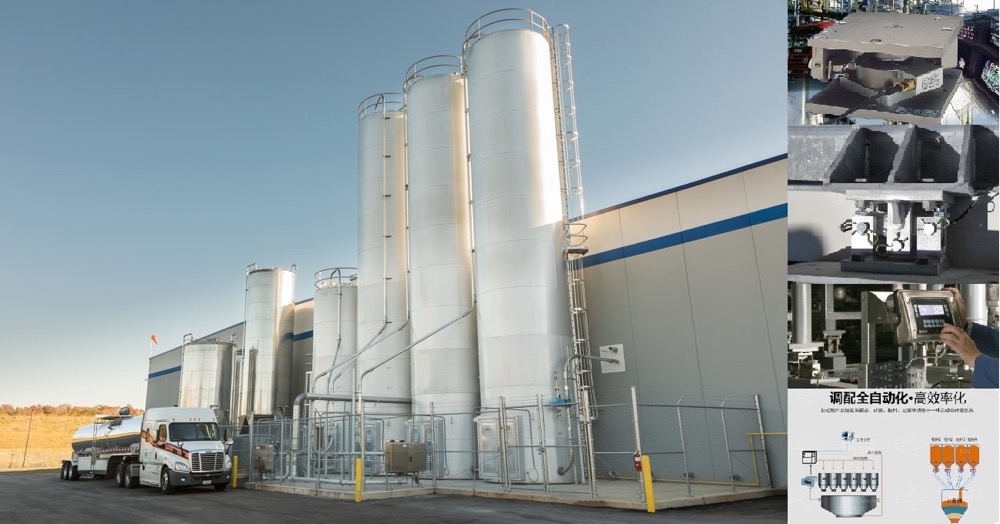
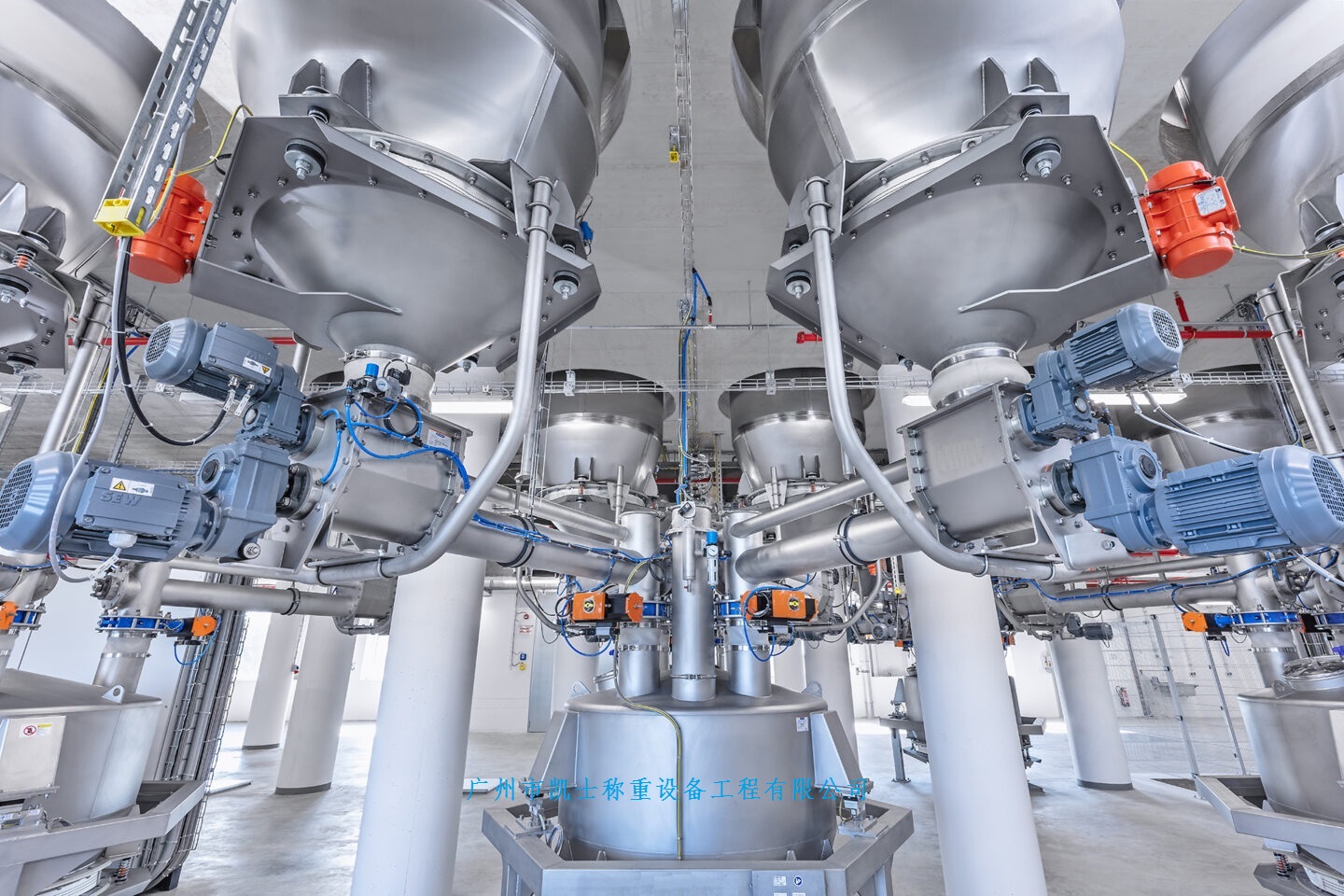
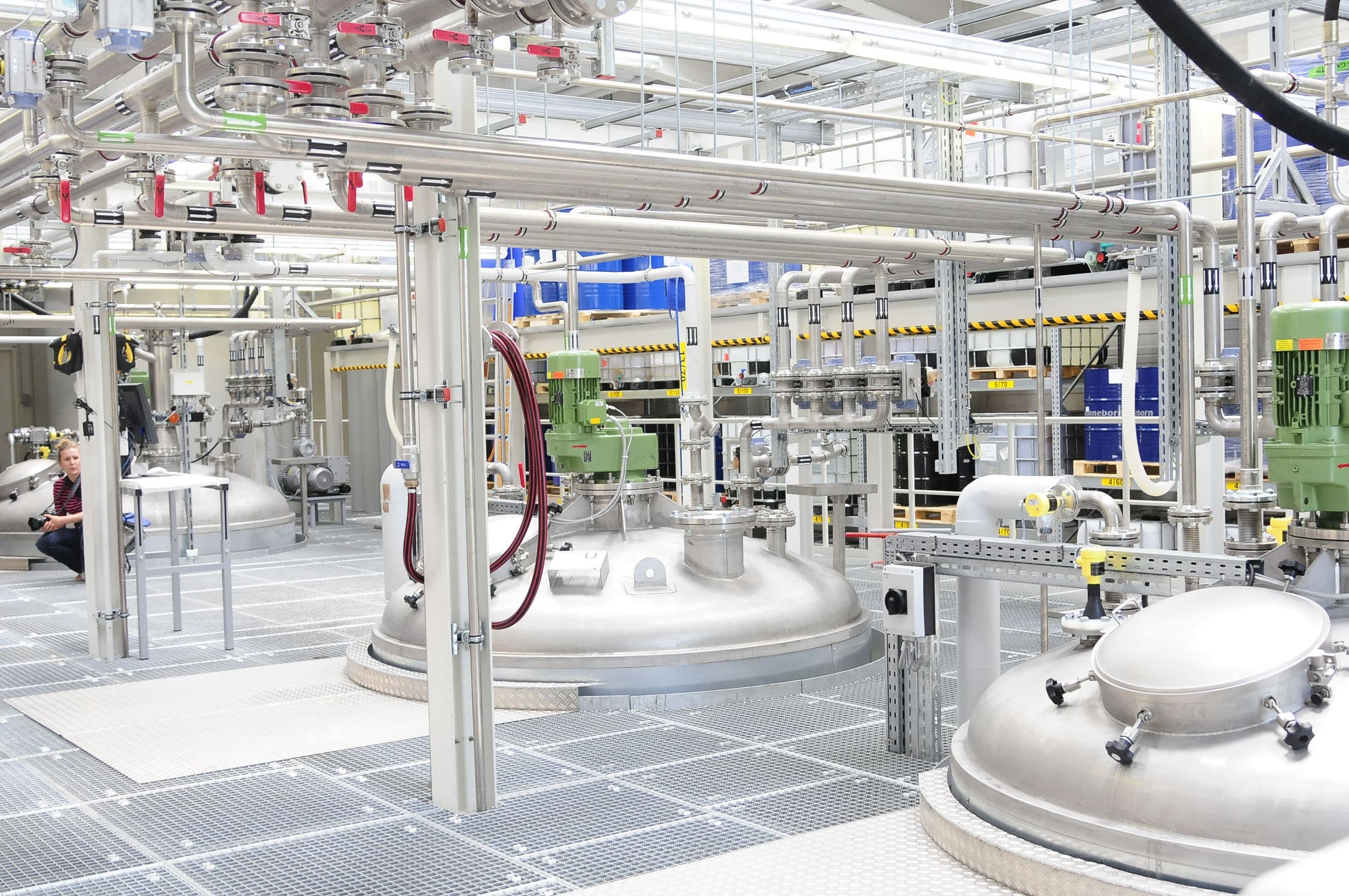
The Computer weighing system is based on a load cell, and through signal amplification and a microprocessor, the weight value is converted into an electrical signal output, which can be used for data processing by a computer. It is suitable for controlling the production process with computerized technology.
 020-34563445
020-34563445The formula, feeding and discharging of the computerized Weighing system are all controlled by the computer. The scale body, apart from the hopper, also includes a dynamic weighing module, a precision amplifier, an analog-to-digital converter, a microcomputer, a display, a printer and an execution system, etc. The touch screen control system can control multiple reaction tanks and agitators, and can also control the time of dry and wet mixing. It can prepare several to dozens of materials, and simultaneously display the batching process and print the names, masses, total masses, cycle times, formulas, daily reports, monthly reports, etc. of each material. The computerized automatic batching production line has a large formula storage capacity, a wide variety of batching types, high speed, high accuracy, and can provide rich software, making program modification convenient. It is a product with a relatively high degree of automation. Through the weighing instrument or touch screen, the required weight of various materials is set. The screw conveyor automatically conveys them in sequence to the Batching system for automatic weighing and flow control, thereby achieving precise measurement and batching.
The control unit of the feeding system adopts an intermittent static weighing principle, that is, each cycle completes the processes of discharging, weighing, discharging, mixing and batching, and discharging again. Due to the fact that this measurement adopts an intermittent static weighing working mode of intermittent feeding and intermittent discharging, to a certain extent, it overcomes the influence of feeding shock, uneven tare weight and zero drift. Depending on the process, the parameter Settings vary, mainly focusing on the output and the proportioning relationship. After the parameters are set, when the system is running, dynamic detection is conducted on each scale to initially determine whether the feeding has reached the set value of the batching. If the set value is dynamically detected, the feeding will be stopped. After the machine stops, it should be buffered for a certain period of time before weighing begins. For the feeding errors caused by dynamic detection and the single batching errors due to other reasons, the reduction of such errors can be achieved through the supplementation of the next batching or certain algorithms.
The entire feeding system can be divided into four components, namely the detection part, the data processing part, the human-machine interface part and the control part. The detection section mainly amplifies the very low signal coming out of the weighing module through a preamplifier, then removes the interference through a filter circuit, and finally converts the analog signal into a digital signal through an analog-to-digital converter and transmits it to the weighing instrument. The human-machine interface section mainly deals with the interaction with the equipment. Firstly, it displays the system operation status through display devices such as monitors. Secondly, it inputs the system operation parameters into the touch screen through input devices such as keyboards. The control section mainly controls the actuating devices through the driver. Among them, the motor is used to control the opening and closing of the door during discharging, while the electric vibrator controls the discharging action. The data processing section is the core of the batching process. It is mainly responsible for coordinating the work of the other three sections and completing data processing tasks. For instance, it converts the signals transmitted by the weighing module into corresponding weight information and displays it through the human-machine interface section. It also controls the start and stop of the motor and the electric vibrator based on the current discharging or discharging status.