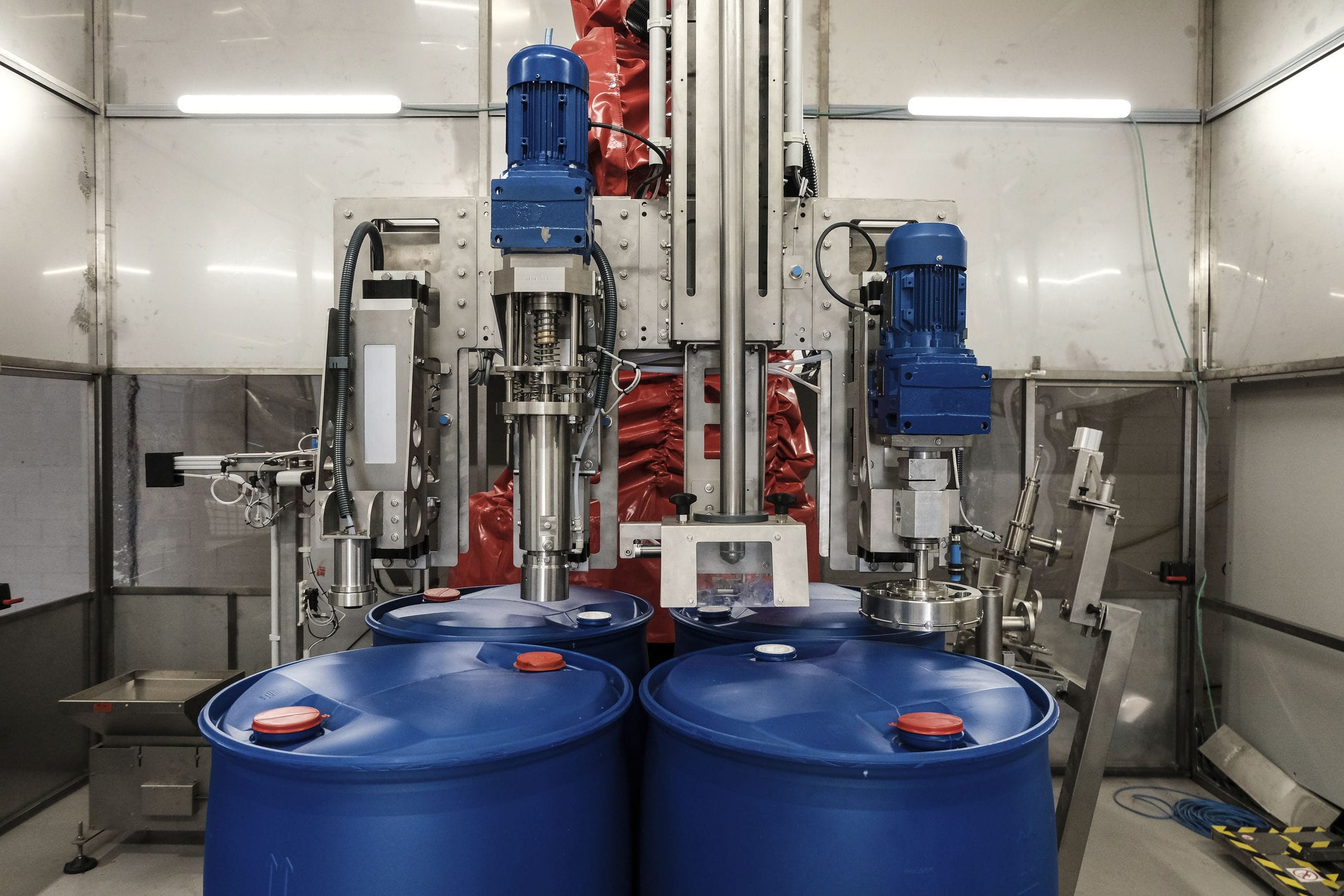
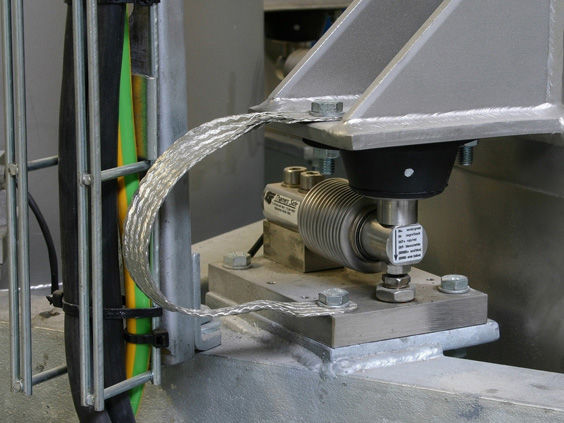
The load cell commonly used in Operation electronic belt scales consists of a load cell bracket that contains a load cell that can detect tension, a load cell bracket that can vary the degree of tension, and a load cell pressure device that can detect variations in the degree of tension. These three components reflect the magnitude of the belt's tension and convert them into an electronic signal output.
 020-34563445
020-34563445Operation Belt scale is in the transportation belt material weight through the weighing frame linear action in the weighing module, so that the sensor in the strain body produces micro-strain, and then will be affixed to the strain body of the bridge on the bridge of each arm of the resistance of the strain gage resistance changes in the supply bridge voltage excitation, there will be an imbalance of the potential output, and at the same time, speed sensors to measure the speed of the belt running, the two signals are sent to the microcomputer accumulator through a series of The two signals are sent to the microcomputer accumulator through a series of operations can be measured after the instantaneous flow of materials. This form is one of the most basic and widely used belt scales, which accepts analog signals from the weighing module and the speed sensor in the system, and displays the instantaneous flow rate and cumulative flow rate after calculation, and at the same time sends the instantaneous flow rate to the computer system as an input signal with a 4-20mA analog current signal, and the computer compares the signal with the set value and outputs a 4-20mA analog current signal through the inverter to control the rotation speed of the feeding motor, which can realize the instantaneous flow rate of the material. The computer compares and calculates the signal with the set value and outputs 4-20mA analog current signal through frequency converter to control the rotational speed of the feeding motor, realizing the closed-loop control of the flow rate of the materials, and finally keeping the instantaneous flow rate and the cumulative flow rate of the materials at the required level of the dosing process.
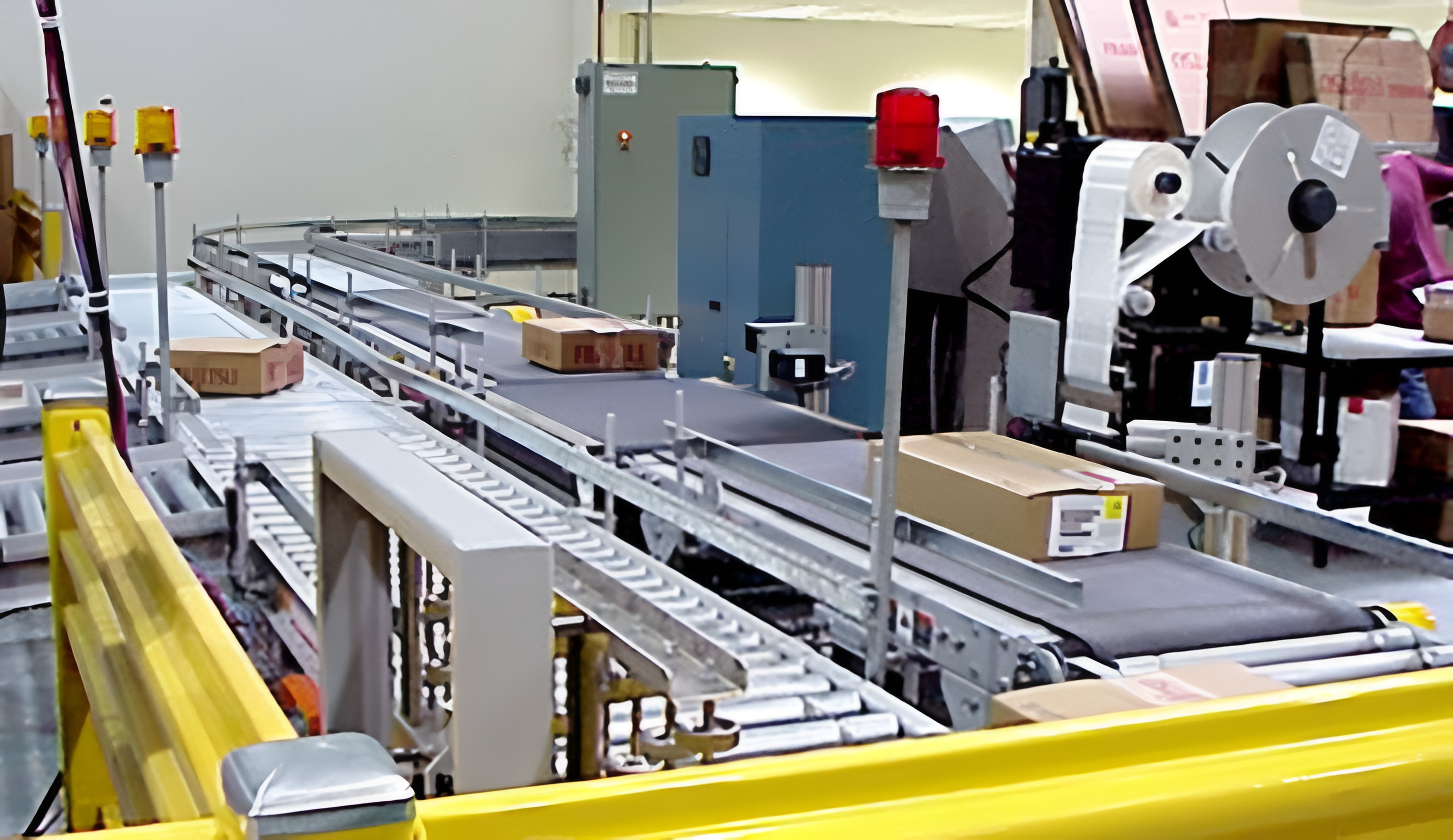
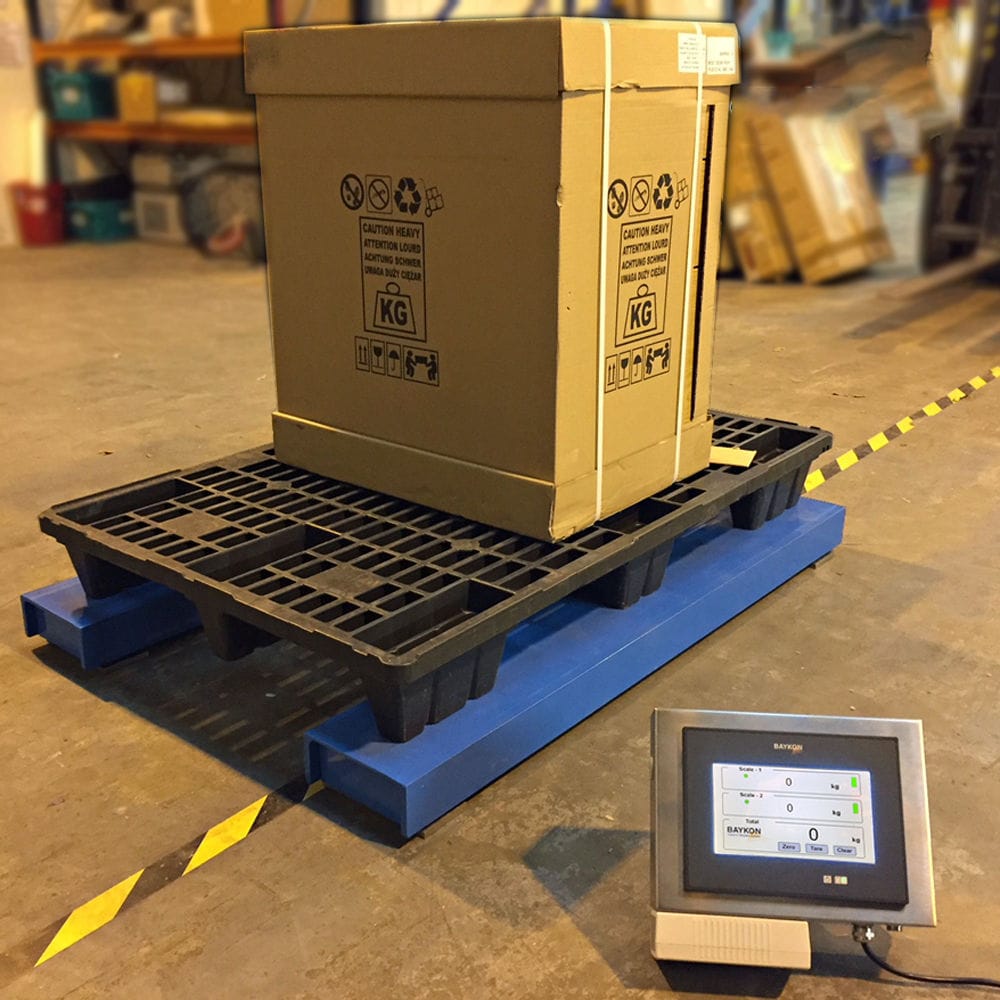
The weighing belt machine consists of a load-bearing device, a weighing module, a speed sensor and a weight indicator. The load-bearing device is responsible for weighing the objects on the belt and transmitting the data to the weighing module, which converts this value into a corresponding voltage signal according to a certain conversion formula, and after a series of processing, converts it into a digital quantity A and transmits it to the operator. The speed sensor receives the speed of the objects on the belt and outputs the pulse number B and transmits it to the operator, which receives the data A, B and then performs the arithmetic processing to derive the total number of objects in a measurement cycle, and counts and accumulates the number of measurements each time to derive the total number of objects that pass through the belt scale.
Belt scale also includes information acquisition part, driving device, information processing part and measuring instrument and so on. The drive device consists of two parts, the frequency conversion motor and reducer, the frequency conversion motor to control the speed of the belt, by changing the speed of the frequency conversion motor belt to change the belt speed to achieve the purpose of changing the speed of the belt, with the reducer to achieve a very good control of the belt speed of the purpose. Nowadays, the more common belt is skirt belt, because it not only has high temperature tolerance but also can prevent the material on the belt from spilling. Such a belt has a high service life and can concentrate the material to avoid unnecessary waste. The carrier can measure the material on the belt and transmit this data (weighing accuracy can reach 1%), with the role of load, measure and gravity transfer. The signal acquisition part is mainly responsible for collecting data, including the data transmitted from the metering module and the speed sensor. The data processing part is mainly responsible for processing the data transmitted to the operator by the weighing module and the speed sensor. Specifically, it includes signal sampling, signal filtering and amplification, A/D conversion, etc. The instantaneous flow rate and cumulative flow rate of the belt scale can be counted, and the flow rate of the belt scale can be adjusted and adapted to the parameter settings according to the results of data processing.