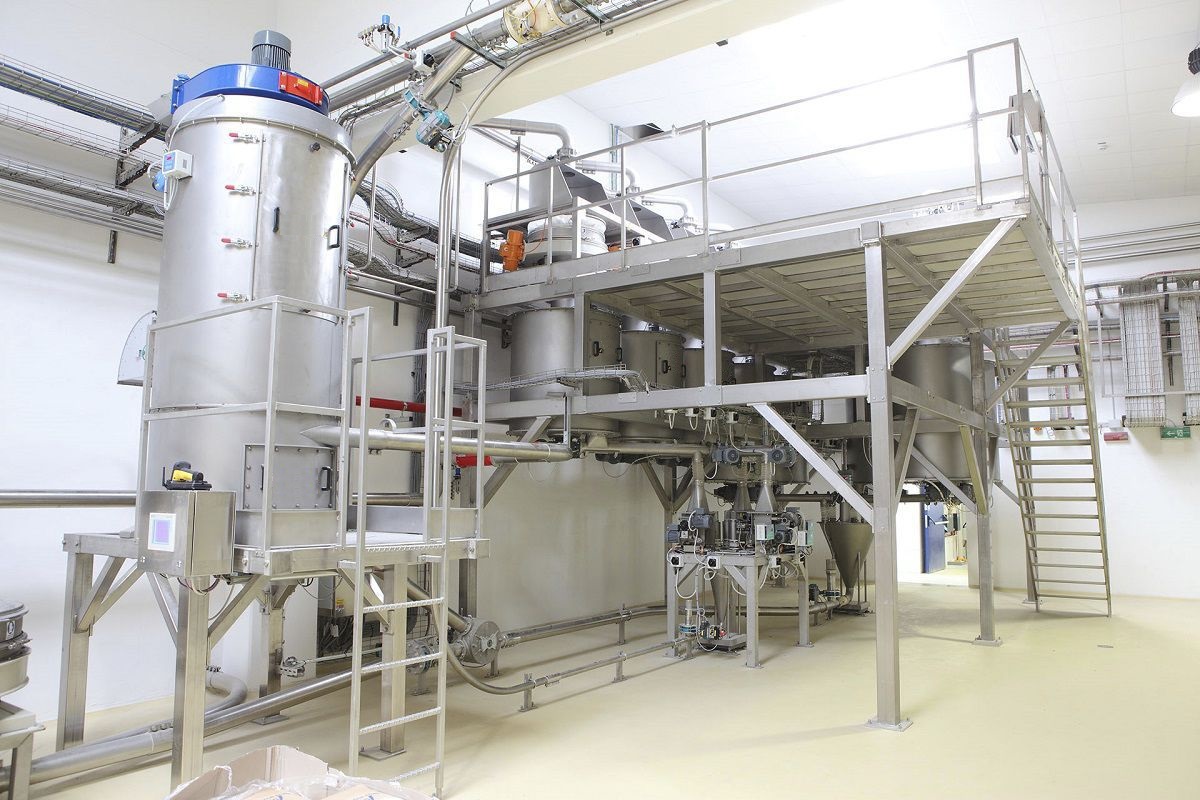
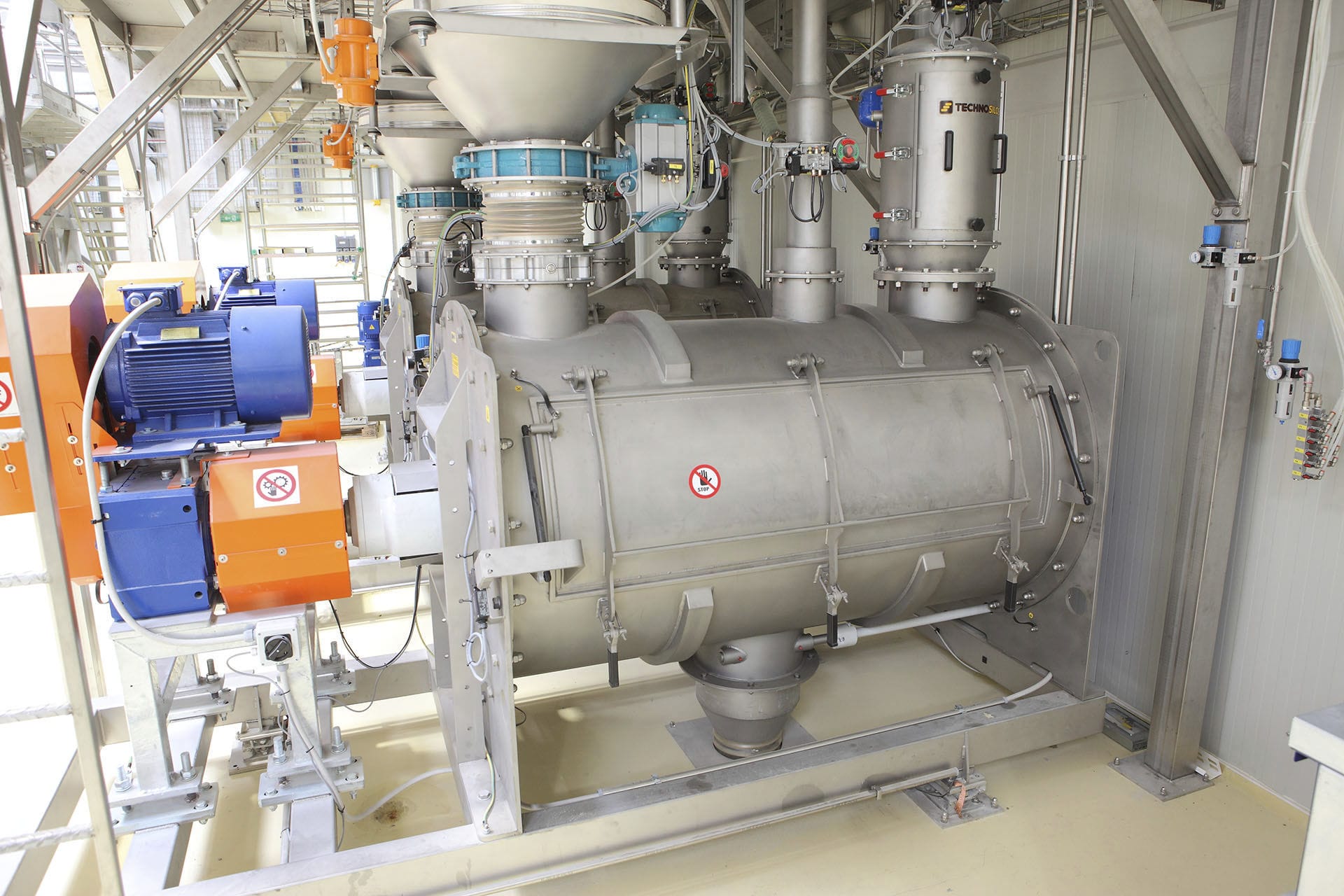
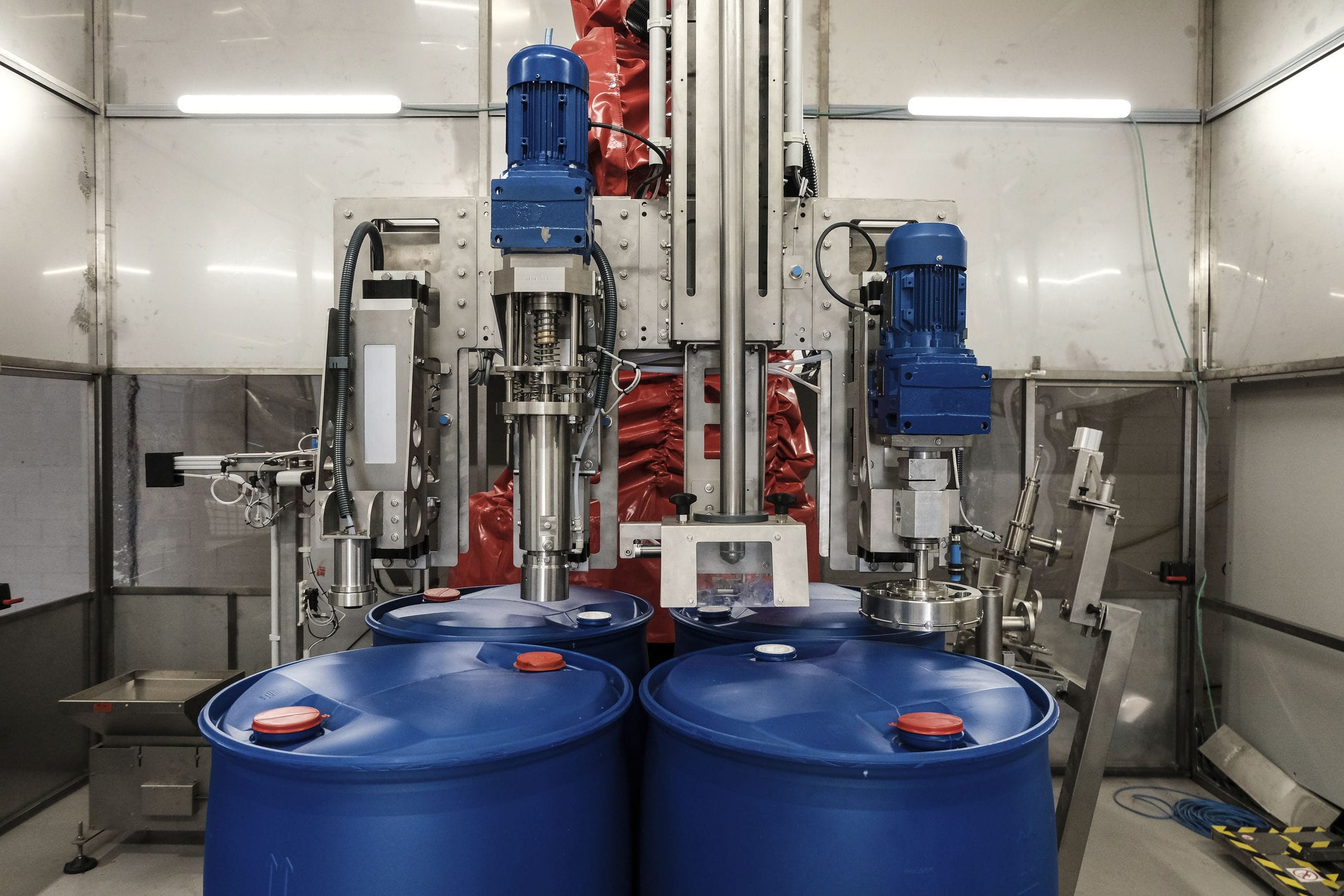
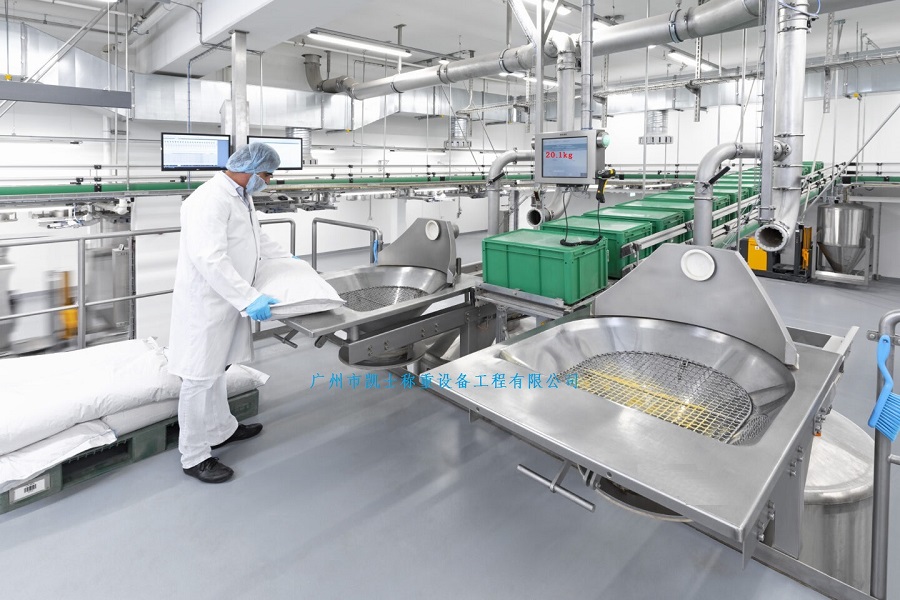
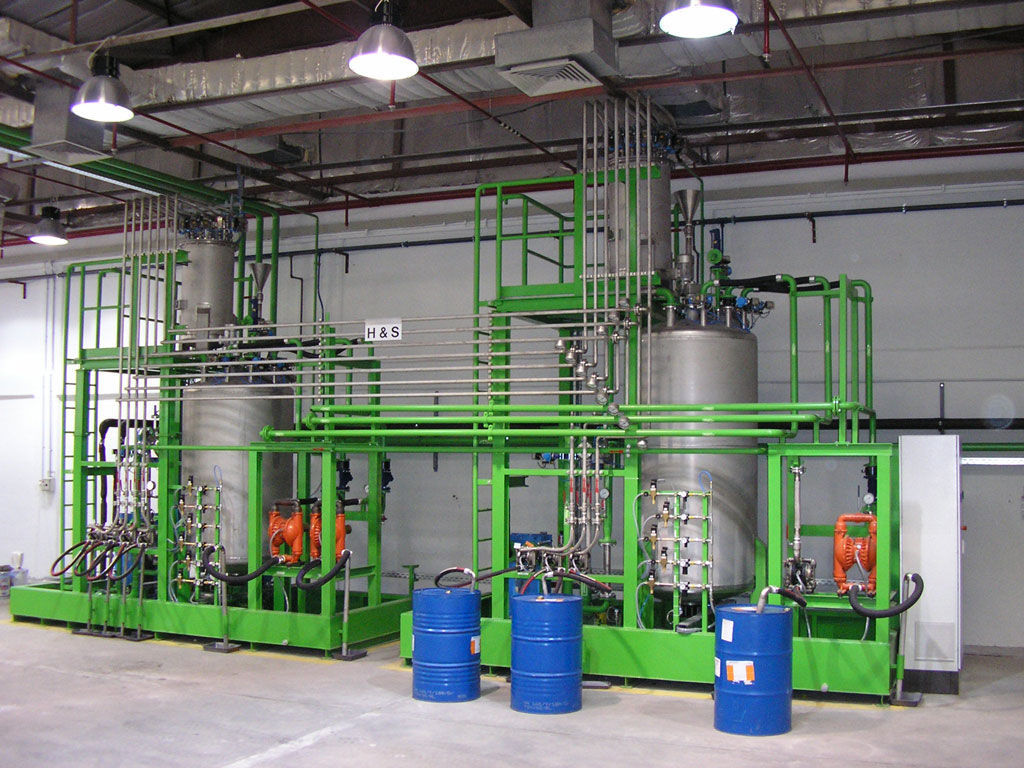
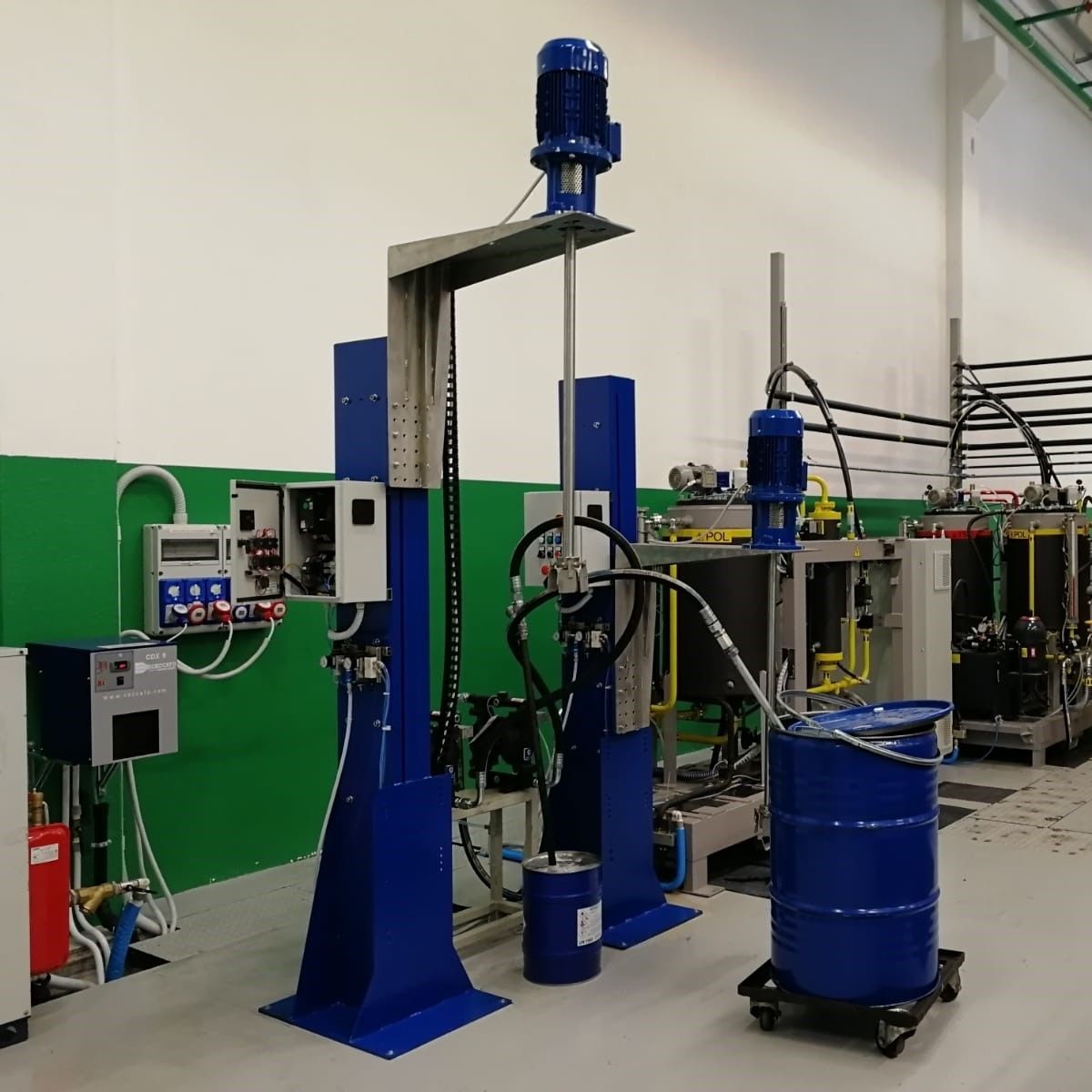
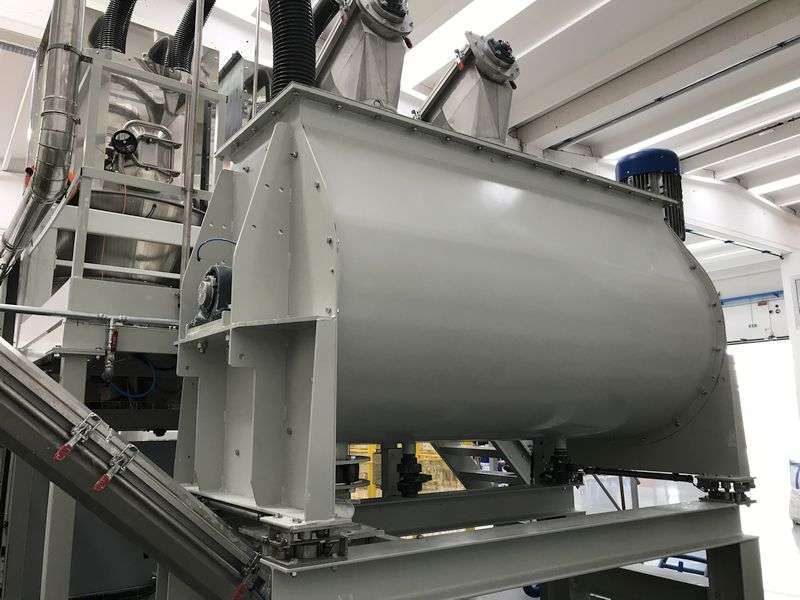
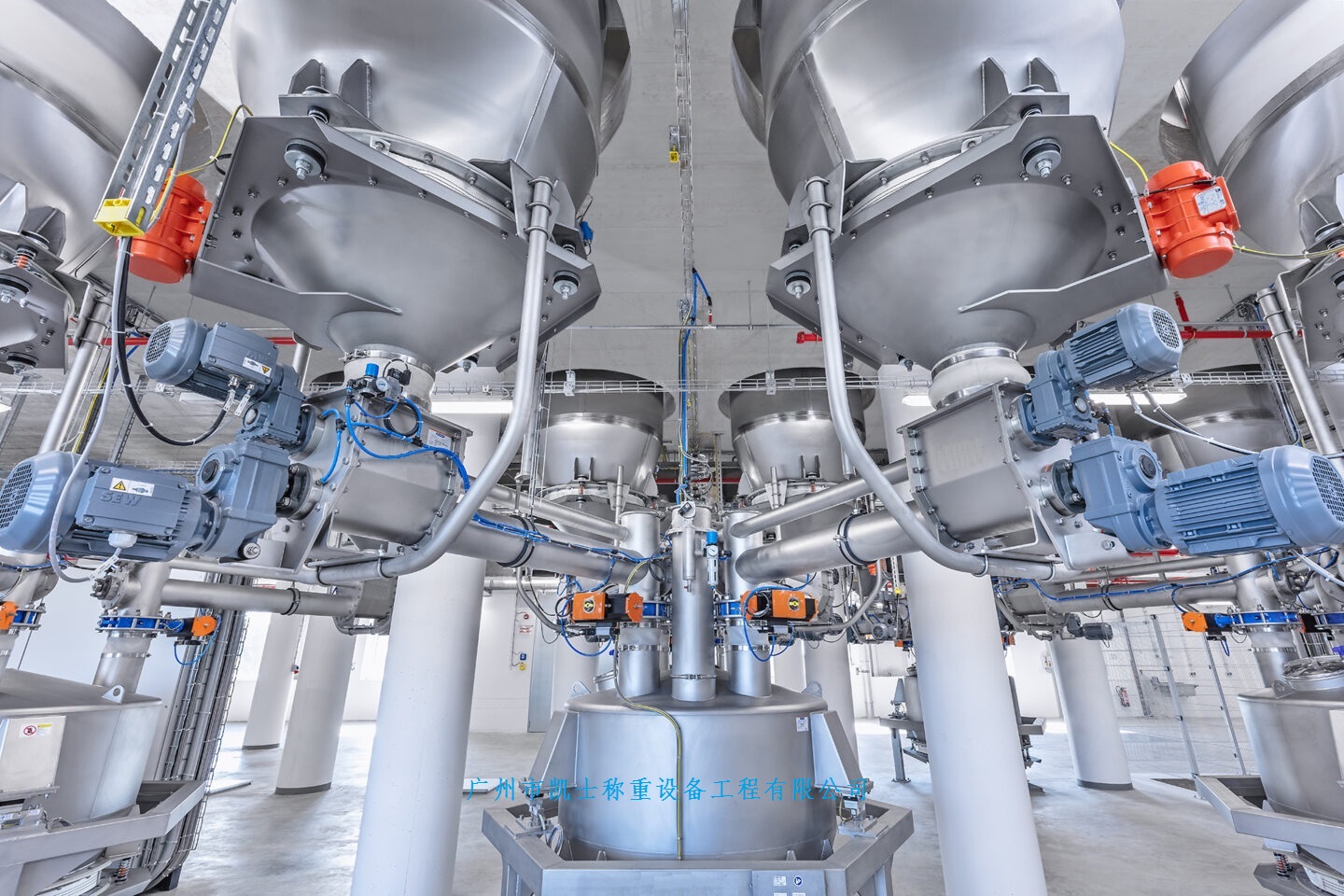
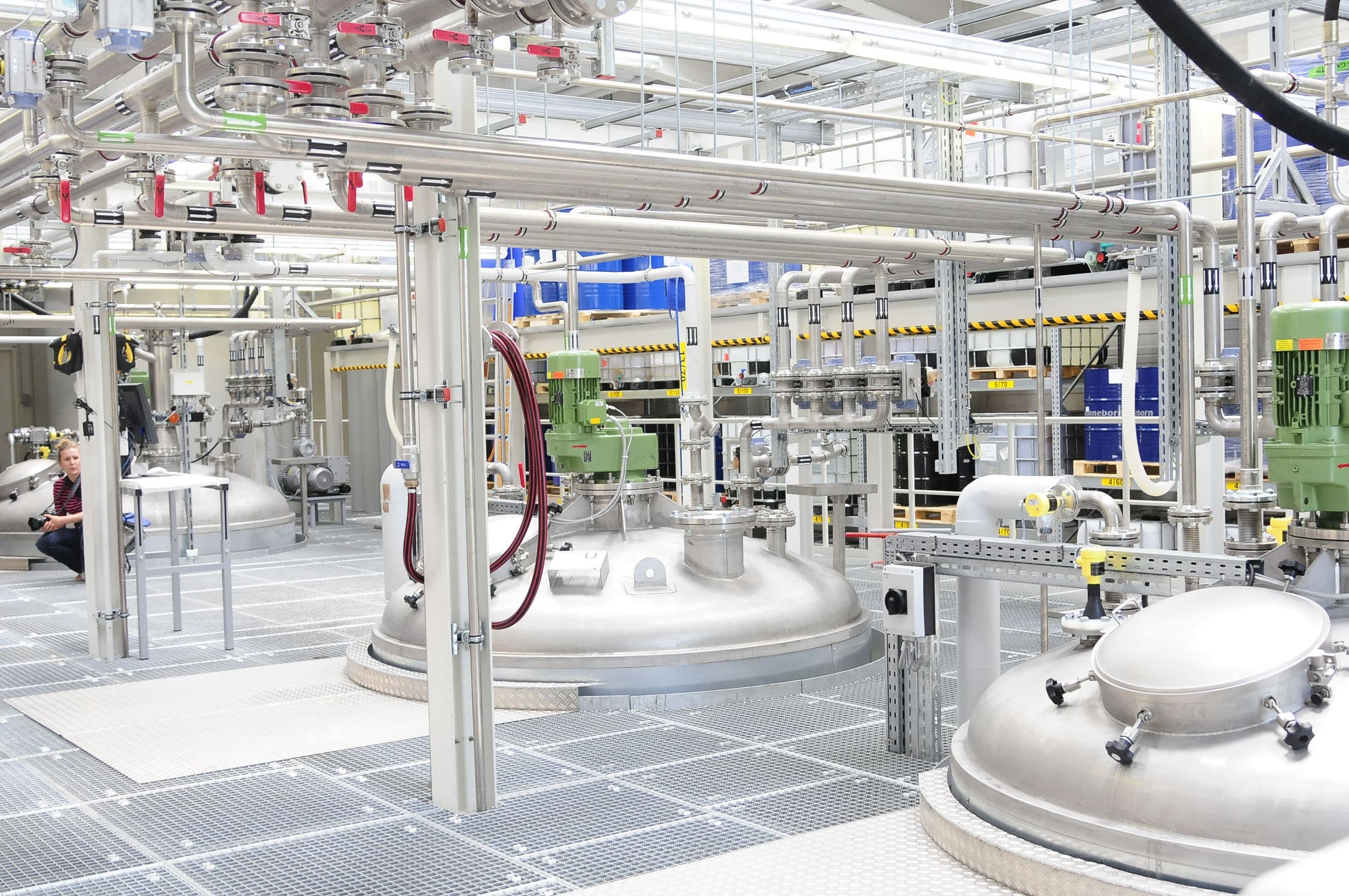
The dosing system is specially designed for the quantitative and proportional packaging of various materials, mixing and dosing in the process. A variety of raw materials proportioning mixed into a rated amount through the automatic proportioning function, the material begins to move when the pre-component will reach 90% of the system automatically turns to slow charging, until the material reaches the precise value of the pre-set parameters, in the process of the weight value of each material is also displayed, then the system automatically opens the discharging arc door and synchronized with the start of the conveyor system will be the material transported to the next unit or for packaging.
 020-34563445
020-34563445Feeding system is specially used in the process of quantitative and proportional packaging, mixing and dosing of many kinds of materials. Many kinds of raw materials are mixed into the rated amount through the automatic proportioning function, the material starts to move when it will reach 90% of the pre-component, the system automatically turns to slow feeding until it reaches the pre-set parameter value of the material precisely, in this process, the weight value of each kind of material is also displayed separately, then the system automatically opens the arc door of discharging, and synchronously starts the conveying system to convey the material to the next unit or for packaging.
The feeding system includes a raw material hopper scale, mixer, central control unit, raw material information acquisition unit and finished product information acquisition unit, the output port of each raw material hopper is connected to the input port of the finished product mixer through the respective weighing module, and all the raw material information acquisition unit and finished product information acquisition unit are electrically connected to the central control unit, and the raw material information acquisition unit collects the information of each raw material according to the set recipe and conveys it to the central control unit. The central control unit selects the raw materials according to the set formula and controls the automatic weighing of the raw materials and then puts them into the finished product mixer, the finished product information acquisition unit collects the information of the finished product and conveys it to the central control unit, which stores the set formula, the raw material information and the finished product information together in the memory. This automatic Batching system realizes the strict control from the quality of raw materials to the quality of finished products, and realizes the control of the production process and the traceability of the quality.
Feeder in advance in refers to the material door closed in the air after the flying material, feeding system using a motor driven eccentric mechanism to produce vibration of the material from the silo added to the hopper, due to inertia when adding material, weighing must be set in the arrival of the target weight before stopping the material motor. The difference between the target weight of the material and the weight of the material at the time of stopping the material is the advance in the feeding control. (Material advance = weight of the material after stopping - weight of the material at the time of stopping)
The amount of advance is not fixed, subject to the influence of many factors, such as the measurement of the Dosage system running fast or slow, the speed of the material falling, the size of the material particles, the viscosity of the material has a close relationship with other factors. Feeding control in advance must follow the real-time situation of the mixer automatically adjusted to ensure the accuracy of the weighing.
In advance of the amount of algorithm model first of all on the signal acquisition digital filtering preprocessing, using recursive average filtering.
Every time the program system calculates the advance amount, it refers to the previous discharging history data, thus obtaining the influence coefficient representing the material falling speed, particle size, viscous degree and other factors, automatically adapting to the operating environment and obtaining the accurate advance amount. The initial value of the preset advance is not necessarily close to the actual value when the machine is first started, but after a few cycles of operation, it will be automatically adjusted to suit the operating environment, so that the system will soon obtain the accurate advance without manual correction.