During the entire measurement process of the bulk material scale, no gate is set at the lower hopper of the scale, and the material is continuously and stably fed to the screw conveyor. The feeding screw conveyor in the upper hopper of the scale also operates continuously and stably. Based on the closing and opening of the gates of the upper hopper of the scale and the hopper scale, as well as the stable time required for the weighing of the hopper scale, static measurement is achieved, while meeting the requirements of continuous conveying.
 020-34563445
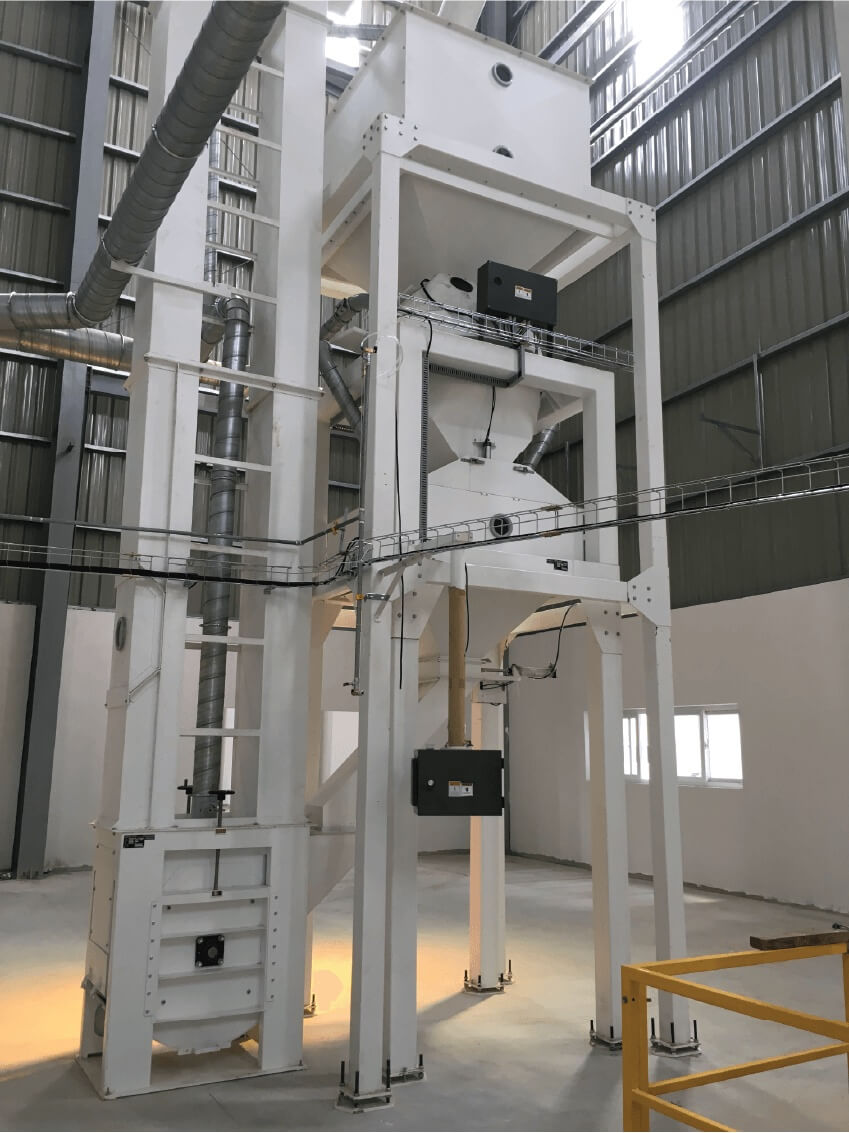
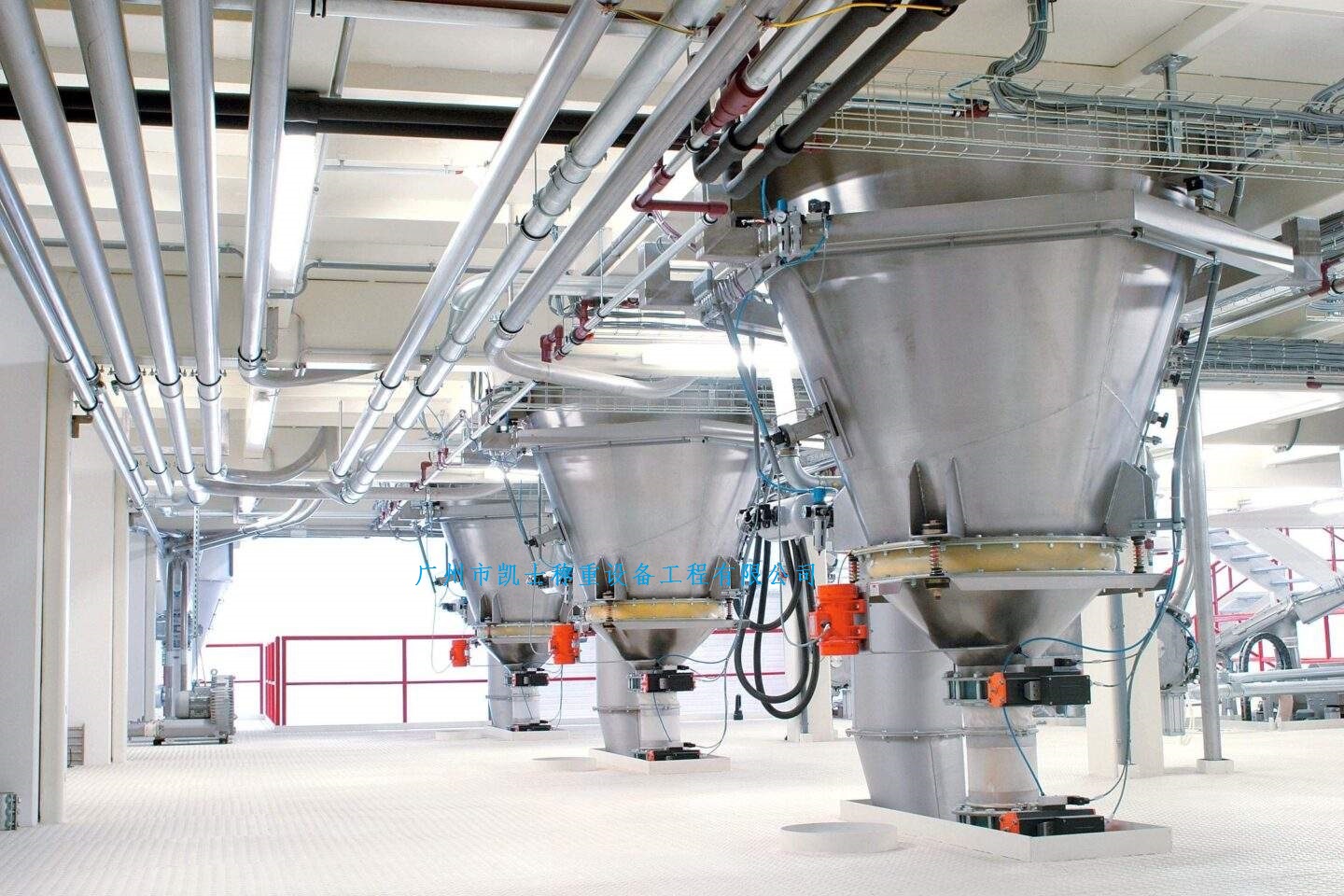
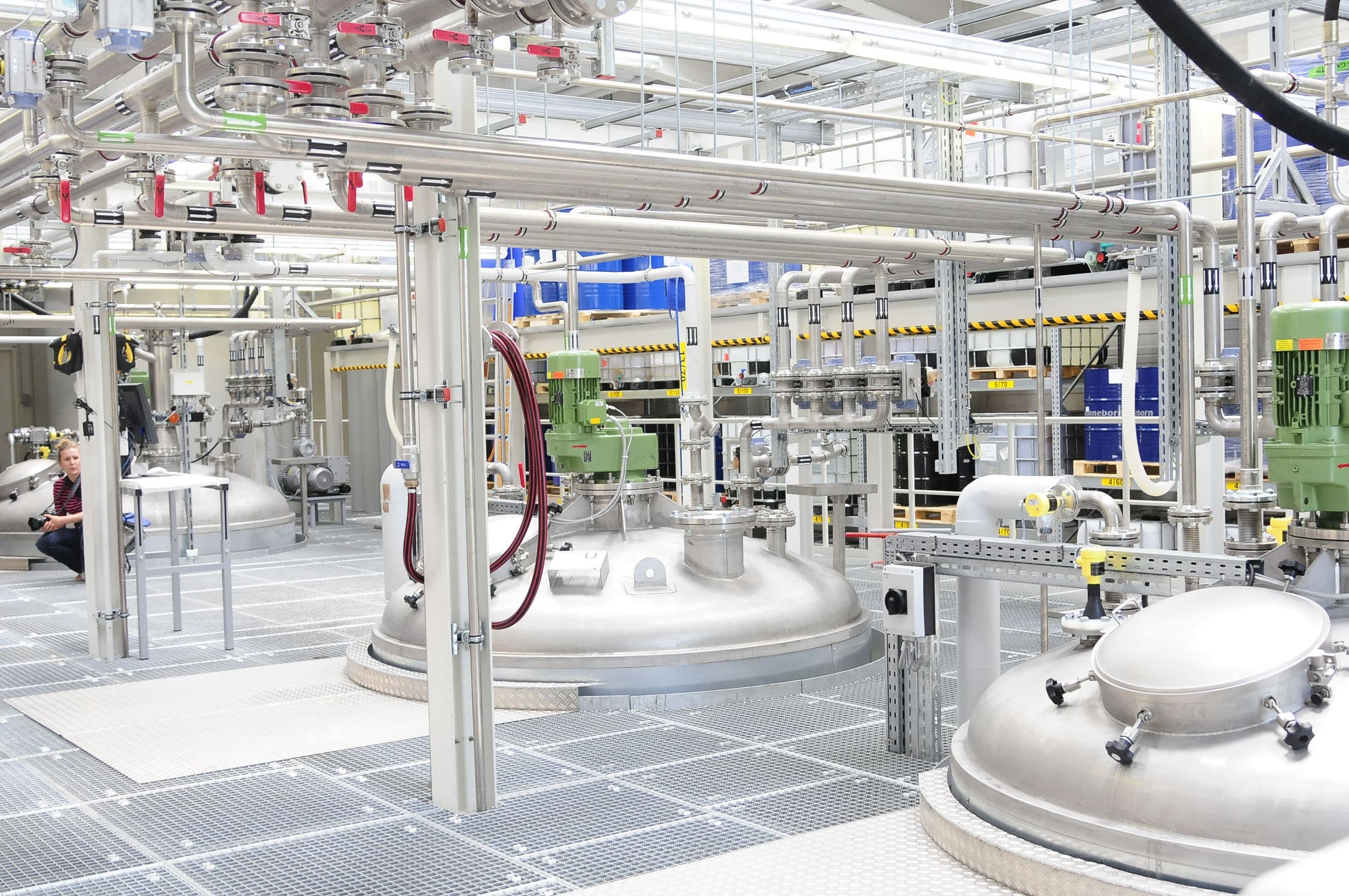
020-34563445Bulk material scales are generally composed of storage hoppers, feeding parts, hopper scales, Weighing modules, unloading hoppers, weighing instruments, etc. The feeding and unloading actions are automatically completed by the weighing instrument controlling the pneumatic mechanism through an electromagnetic network. No manual intervention is required during the execution process or at the operation site. When the system conditions are met and the automatic operation begins, the feeding door opens. The material flows from the upper hopper to the hopper scale (feeding cycle). When the preset material weight is reached, the feeding door closes, and the weighing instrument of the scale records the weight of the material inside the hopper scale (gross weight record). Then, the discharge door opens to unload the material from the hopper scale to the lower hopper (unloading cycle). After the hopper scale has discharged the material, the discharge door closes. The weighing instrument records the weight of the remaining material in the hopper scale (tare weight record). After recording the gross weight and tare weight, the program calculates the net weight of the material and starts the next weighing. After each weighing, its net weight is added to the previous cumulative net weight. When the cumulative net weight reaches the preset weight, the weighing process will automatically stop.
When the hopper scale is empty, close the gate at the upper hopper of the scale to automatically reset the hopper scale. The material conveyed by the screw conveyor enters the upper hopper of the scale. During the feeding process, close the gate at the hopper scale and open it. The material enters the hopper scale from the upper hopper of the scale and then enters the feeding section. When the required weight for each scale is reached during the weighing process, the gate at the upper hopper of the scale is closed for weighing and measurement. The weight value of the scale is automatically stored and accumulated. Discharge process: After the measurement is completed, the gate at the scale of the hopper opens, and the material is discharged into the lower hopper of the scale. When the hopper scale has completed discharging materials, the gate at the hopper scale closes, automatically zeroing the hopper scale and entering the next weighing cycle. Throughout the entire measurement process, there is no gate at the lower hopper of the scale, which continuously and stably feeds the screw conveyor. The feeding screw conveyor in the upper hopper of the scale also operates continuously and stably. Based on the closing and opening of the gates of the upper hopper of the scale and the hopper scale, as well as the stable time required for the weighing of the hopper scale, static measurement is achieved, while meeting the requirements of continuous conveying.
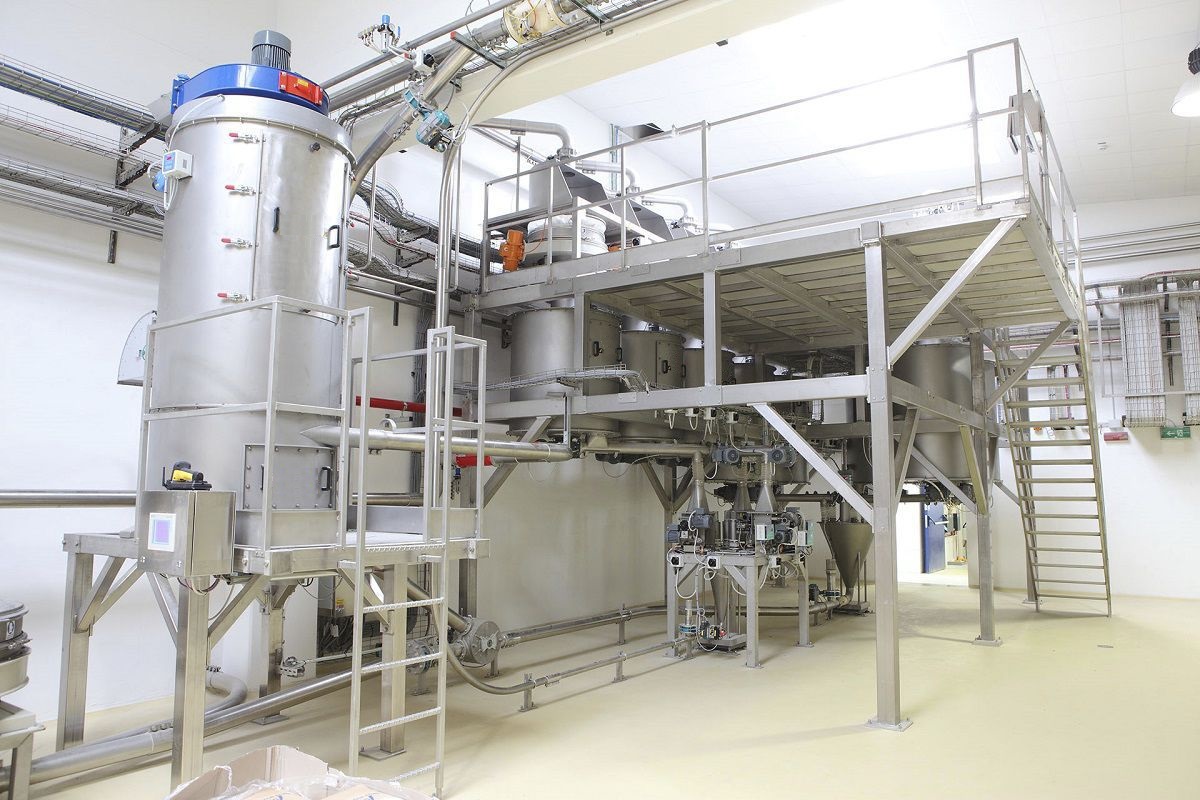
Storage hopper
To ensure a constant flow rate of materials, a storage hopper must be installed above the non-continuous accumulation scale. The capacity of the storage hopper should be able to hold at least two maximum scales of materials. Usually, a level gauge is installed to ensure that the storage hopper has sufficient materials. The level gauge can be connected to the control cabinet of the scale. The storage hopper is connected to the feeding part of the non-continuous cumulative scale through a flange, so that the hopper scale does not bear the weight of this part.
Unloading hopper
The material discharged from the hopper scale should be completely fed into the discharge hopper without reservation; otherwise, the remaining material will be mixed with the material to be weighed in the next time. To avoid this situation, the storage capacity in the discharge hopper should be at least the maximum amount of material for one weighing. Therefore, a level gauge needs to be installed in the discharge hopper. This level gauge should be connected to the control cabinet of the scale. The hopper scale will only release the material when there is sufficient space in the discharge hopper.
Feeding section
At the bottom of the feeding section, there is one or two sector-shaped feeding doors, which are driven by one or two cylinders. The cylinders are controlled by solenoid valves. The opening position of the feeding doors is detected by proximity switches. The feeding speed is determined by the opening degree of the feeding doors. According to the density of the material, the values of coarse feeding and fine feeding of the material can be set to optimize the batching weight. Adjust the two-stage feeding rate.
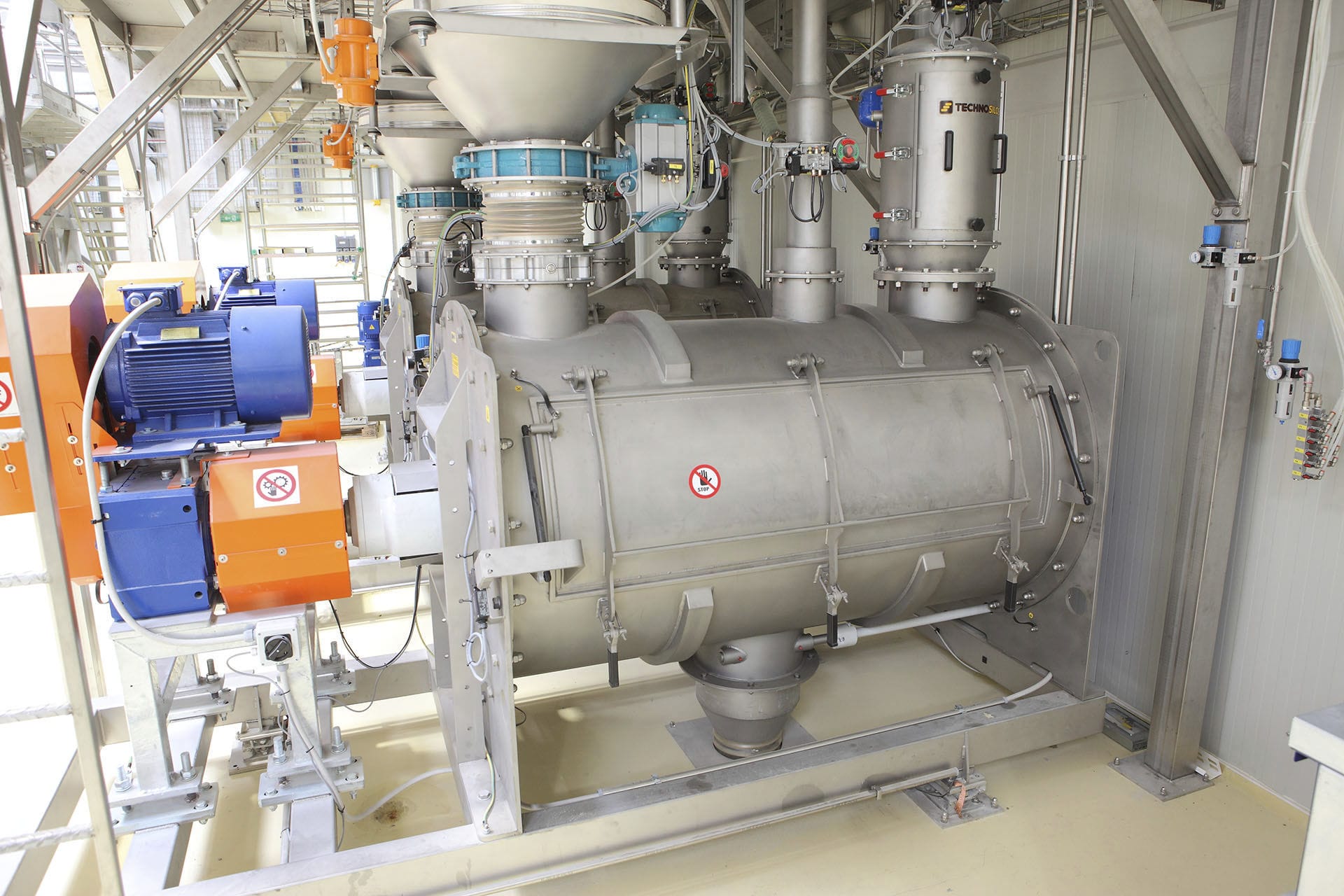
Hopper scale
At the bottom of the hopper scale, there is one or two sector discharge doors - the discharge doors are driven by a cylinder, which is controlled by an electromagnetic valve. Inside the hopper scale, there is a height-adjustable material level gauge. The upper part is suspended from the feeding section, and the lower part is placed vertically in the hopper scale to prevent the material inside the hopper scale from overflowing due to excessive feeding flow rate or other reasons. The closing position of the discharge door is detected by a proximity switch.
When feeding and unloading materials, the hopper scale has an internal air balance tube to compensate for the pressure difference and reduce the influence of air pressure on weighing. The balance tube is equipped with an automatic vacuum door to allow air to enter during dust removal. Both sides of the hopper scale are also equipped with weight platforms for placing calibration weights. To facilitate the calibration of scales by the metrology department during trial operation, initial appraisal and subsequent inspection, a platform for testing weights can also be suspended from the hopper scale and placed at a lower horizontal position to simplify the testing process. Inside the hopper scale, detachable wear-resistant liners are installed at the areas affected by material flow impact and wear. Different wear-resistant liners can be selected according to different materials, such as wear-resistant steel plates, stainless steel, and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, etc.
Weighing instrument
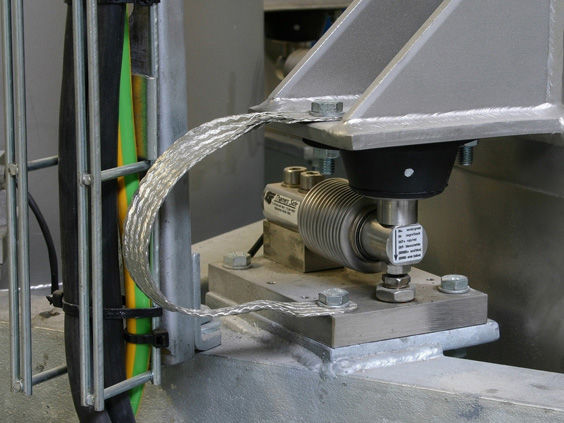
The weighing instrument provides weight measurement. The user dialog box and the weighing process control controller can be installed near the hopper scale or in the centralized control room. The controller is equipped with a microprocessor to control the weighing process and also features an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Data transmission between the controller and the control box can be achieved through a serial connection RS485. The operator inputs process parameters and necessary operation data through the operation keyboard to achieve human-machine dialogue. Control commands for the weighing process can be given through function keys according to different weighing statuses and can be dynamically displayed in graphics and text on the screen. It can be connected to an external printer to print the weighing data and corresponding process parameters.