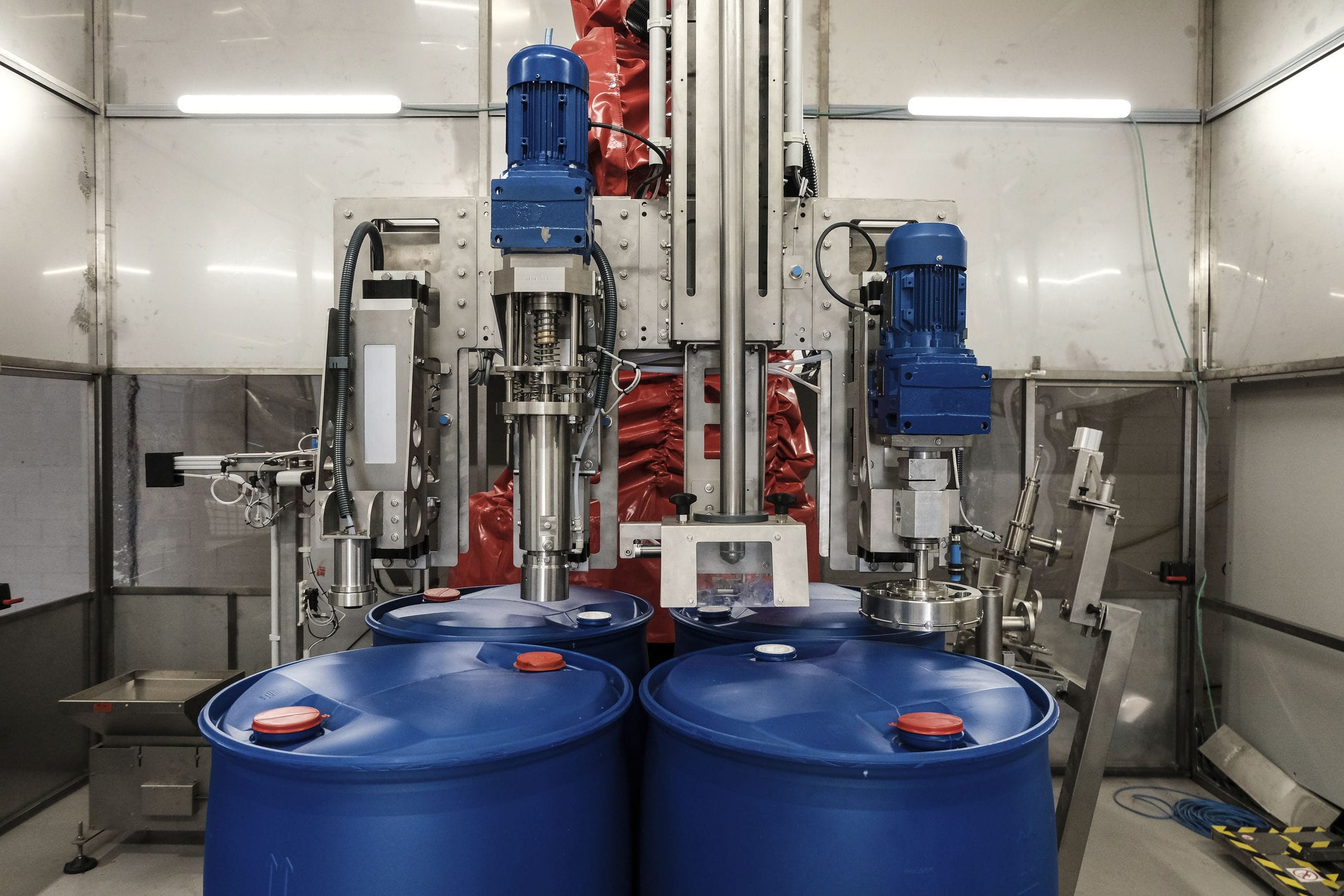
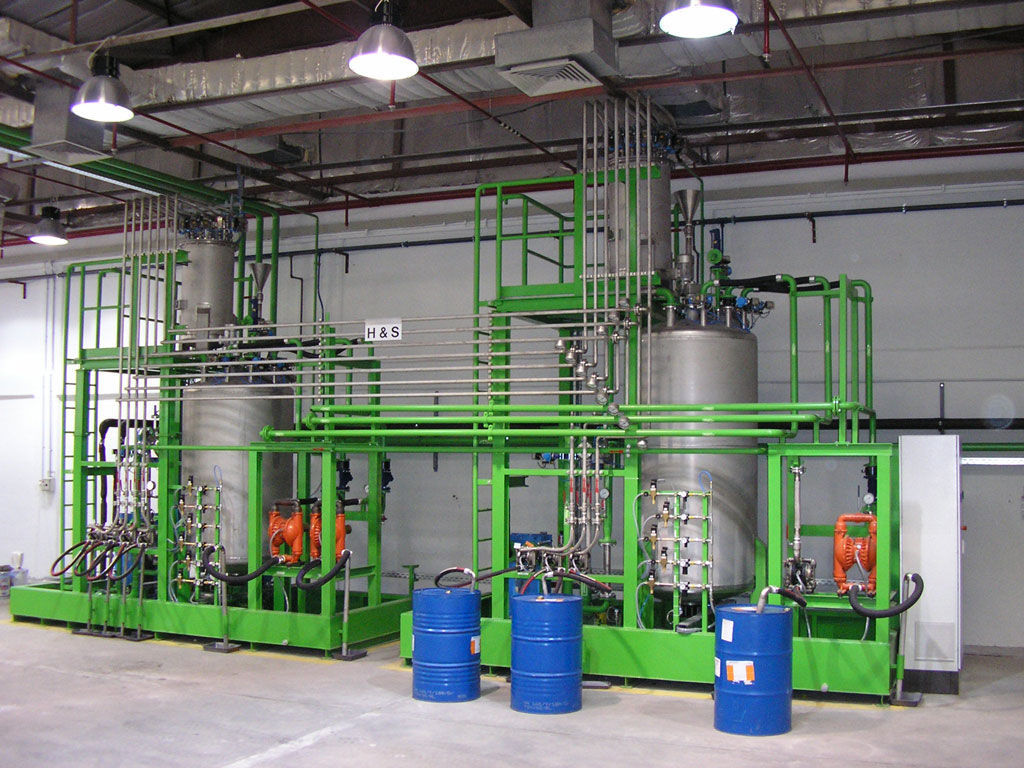
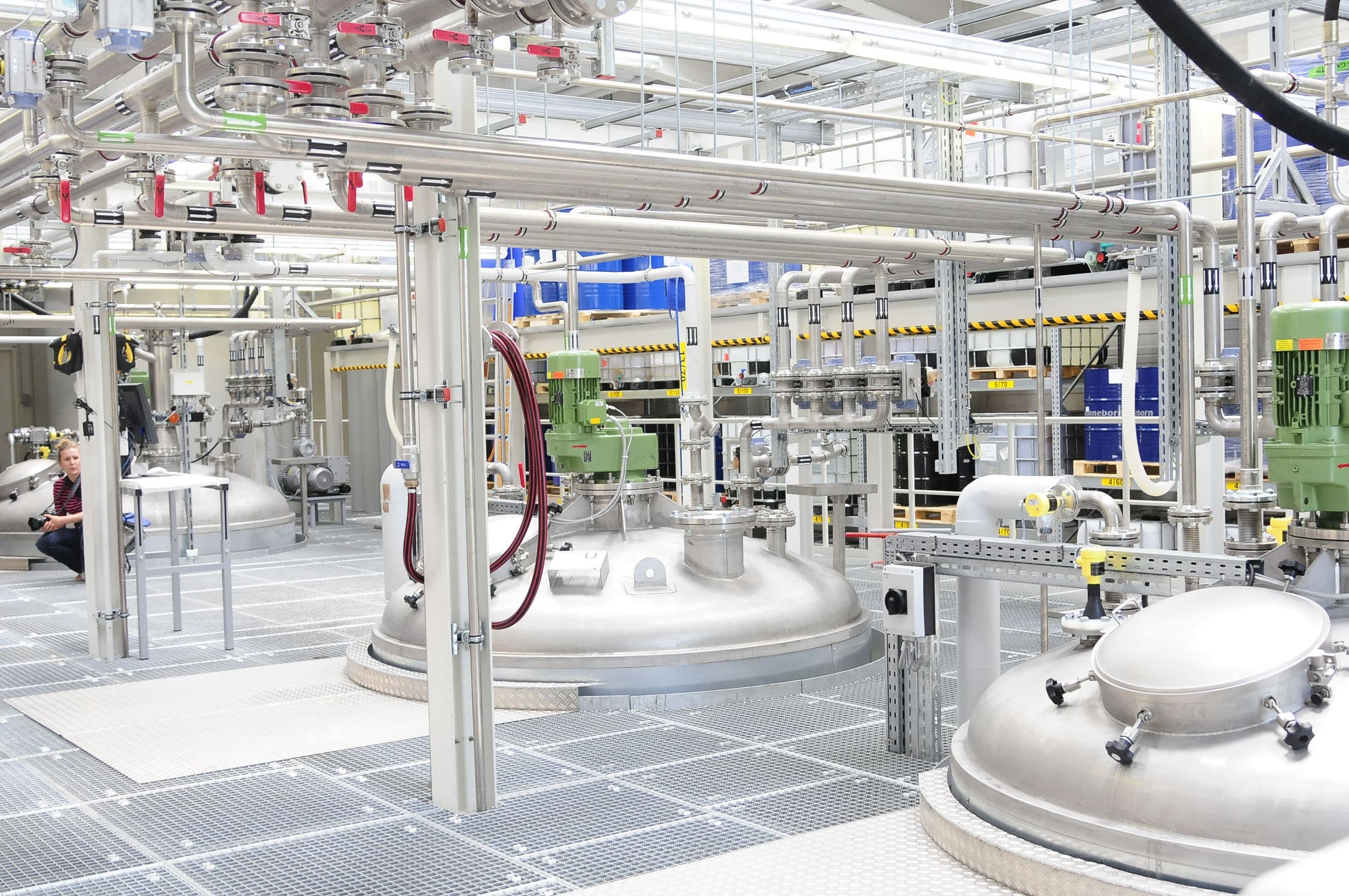
The double-flow liquid filling machine adopts a microcomputer control processing method to achieve full automation and intelligence in the filling process. It can complete actions such as increasing distance, reducing distance, diverting, lifting and turning over of regular or irregularly arranged batch filling containers according to the filling process requirements, and then convey them to the scale platform of the filling actuator to complete the cylinder lifting filling.
 020-34563445
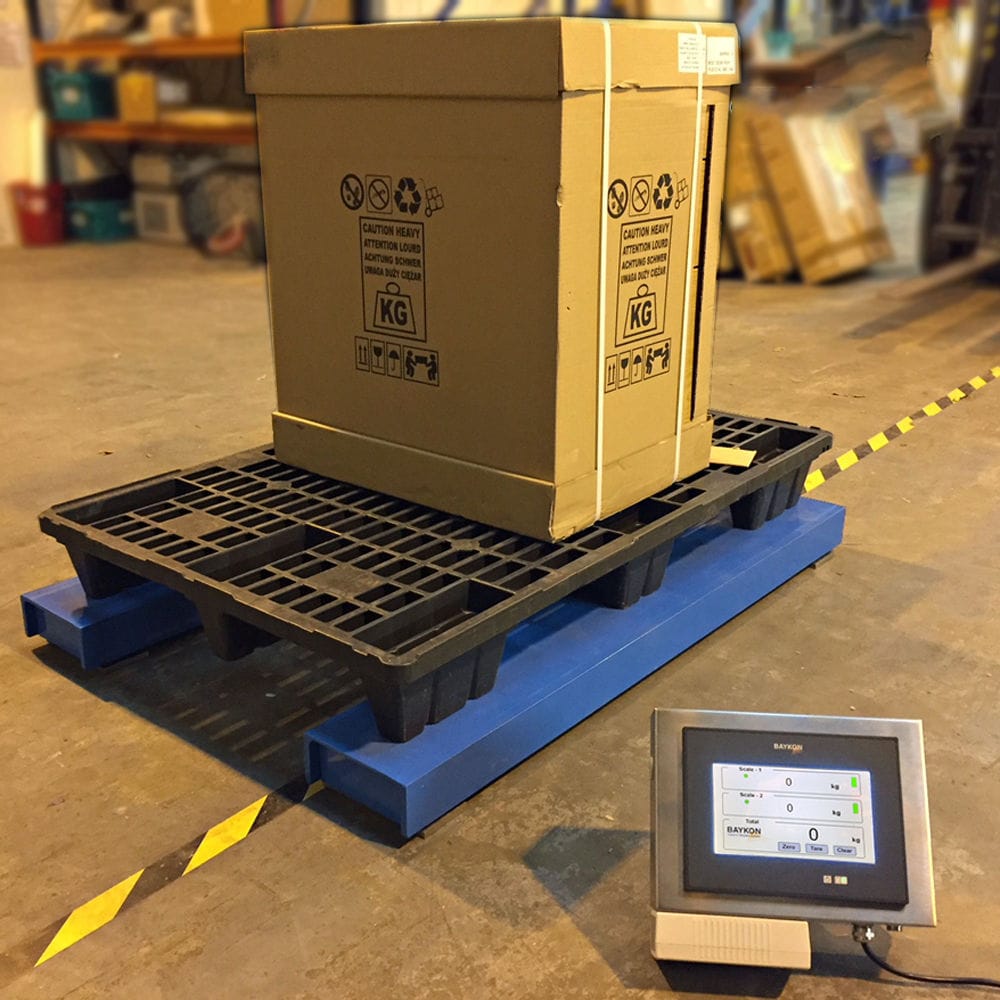
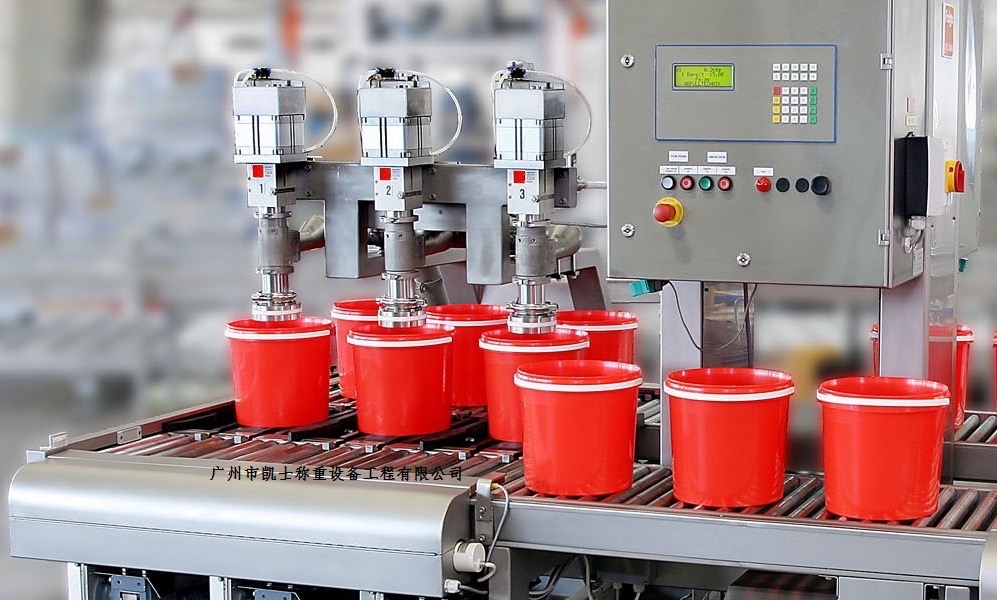
020-34563445The double-flow liquid Filling machine selects the filling volume by the computer Filling system, adds empty barrels for filling, and records and binds the information through RFID. The weight information of the material barrels is read by an RFID reader. When the difference in weight information exceeds the standard, it is determined that the filling is abnormal and they cannot be stored in the warehouse but are removed to the platform for handling. When the difference in weight information between the two does not exceed the standard, it indicates that the filling is undamaged and free of impurities, and it is allowed to be stored in the warehouse. At the filling site, there is a platform scale equipped with rollers. During the conveying operation, it is determined whether the empty barrels on the platform scale are in place. On both sides of the scale platform, direct-beam photoelectric switches are installed. After the operator selects the barrel entry operation, the empty barrels are conveyed to the material receiving position, which blocks the photoelectric switch and sends a signal to the PLC. At this time, the PLC begins to complete the tare operation. After completion, the photoelectric indication is fed back to the filling machine operator. The filling process is allowed to start. Once the set weight is reached, the machine will automatically stop to complete the discharge operation from the material bucket and then proceed to the transfer conveyor line.
The automatic filling machine adopts a three-speed feeding method. It is controlled by a frequency converter to operate the PLC. Through different combinations of output switch quantities, the frequency converter is controlled for frequency conversion speed regulation, achieving rapid feeding, slow feeding and precise feeding. At the beginning of weighing, feed quickly. When the predicted speed of rapid feeding is reached, start feeding slowly. When the slow feeding prediction is reached, start the fine feeding. When the total weight of the feed reaches "target weight - pipeline material weight - allowable error", stop feeding. Among them, the pipeline material weight refers to the material weight remaining in the pipeline and continuing to flow into the weighing tank after the pneumatic valve stops rotating.
The automatic filling machine adopts a microcomputer control processing method to achieve full automation and intelligence in the filling process. It can complete actions such as increasing distance, reducing distance, diverting, lifting and turning over of regular or irregularly arranged batch filling containers according to the filling process requirements, and then convey them to the scale platform of the filling machine to complete the cylinder lifting filling. At the injection pressure port of the liquid, due to the sudden release of pressure, certain resistance around the flow (friction, pressure difference, ripple, induction) will be generated. The greater the pressure, the greater the control error. By changing from concentration to dispersion, from one large hole to multiple small holes, and making the sum of the small hole areas greater than that of the large hole, the flow resistance around is minimized. By adjusting the distance between the pressure port and the return liquid port, the adjustment amount during debugging is increased, and the valve size is controlled by closing the valve to achieve the filling accuracy.
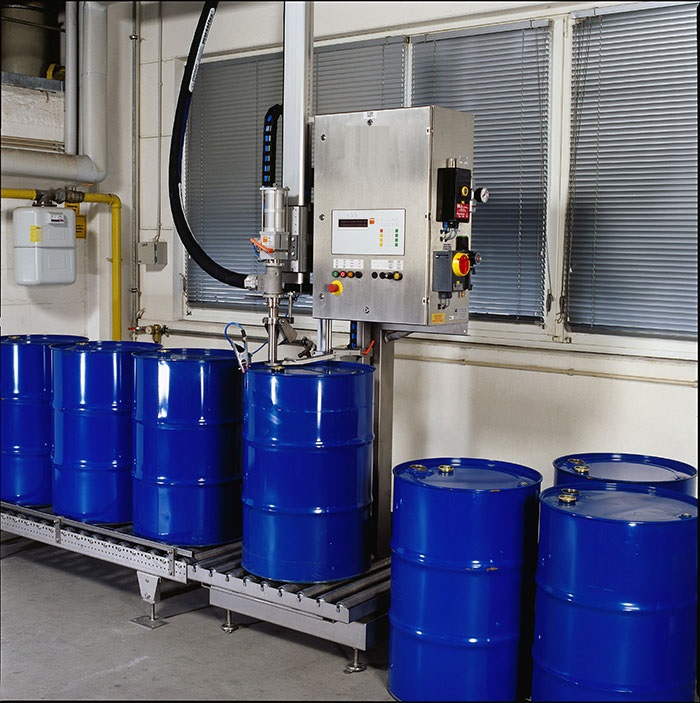
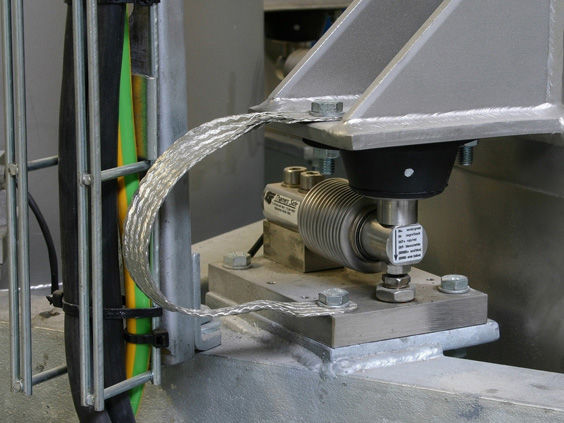
The Weighing system uses a roller conveyor to transport empty drums to the designated filling station. Once the empty drums reach the filling station, the position sensor detects that the empty drums have reached the designated position and feeds back to the PLC. The PLC controls the filling system to fill the empty drums with liquid through logical control instructions. At the same time, the weighing module measures. Once the set filling quality is reached, the push rod of the filling machine is activated to close the filling valve. The filled material bucket is conveyed through the chain plate to the capping system. The cap feeding cylinder extends to move the bucket cap to the designated position. Then, the cylinder drives the slider to slide down on the guide rail, moving the rotating shaft to the grasping position. The bucket lid is lifted by a pneumatic three-jaw gripper. The cylinder pushes the rotating shaft to rise to the designated height, then the bucket reaches the capping position. The rotating shaft descends, and the servo motor drives the gripper and the bucket lid to rotate as a whole to perform the capping operation. After rotating to the correct position, release the clamping gripper, rotate the cylinder to reset, and perform the second rotational tightening action.
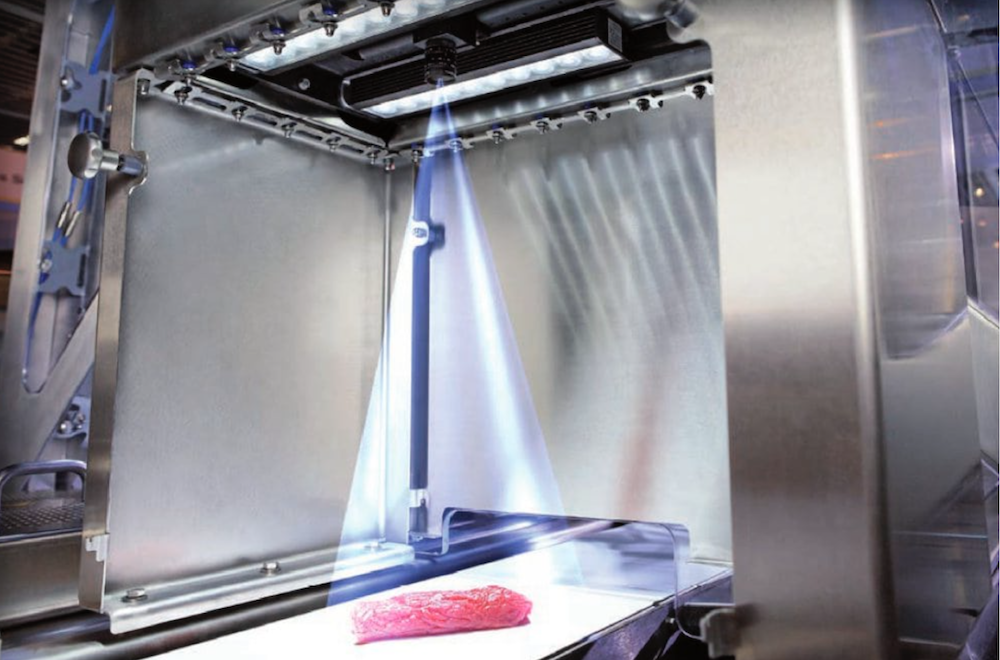
After the filling machine completes the capping tightening action, the gripper that fixes the barrel body reaches the labeling process through the conveyor chain plate. When the Hall element detects the product, the labeling machine works and performs spinning and labeling on the barrel body. The chain plate drives the bucket to the inspection station for inspection, and the labels are inspected through the CCD camera. The control and coordination of each process and action in the entire verification platform, including filling, spinning and sealing, labeling, and inspection, are jointly controlled by the PLC and the upper computer.