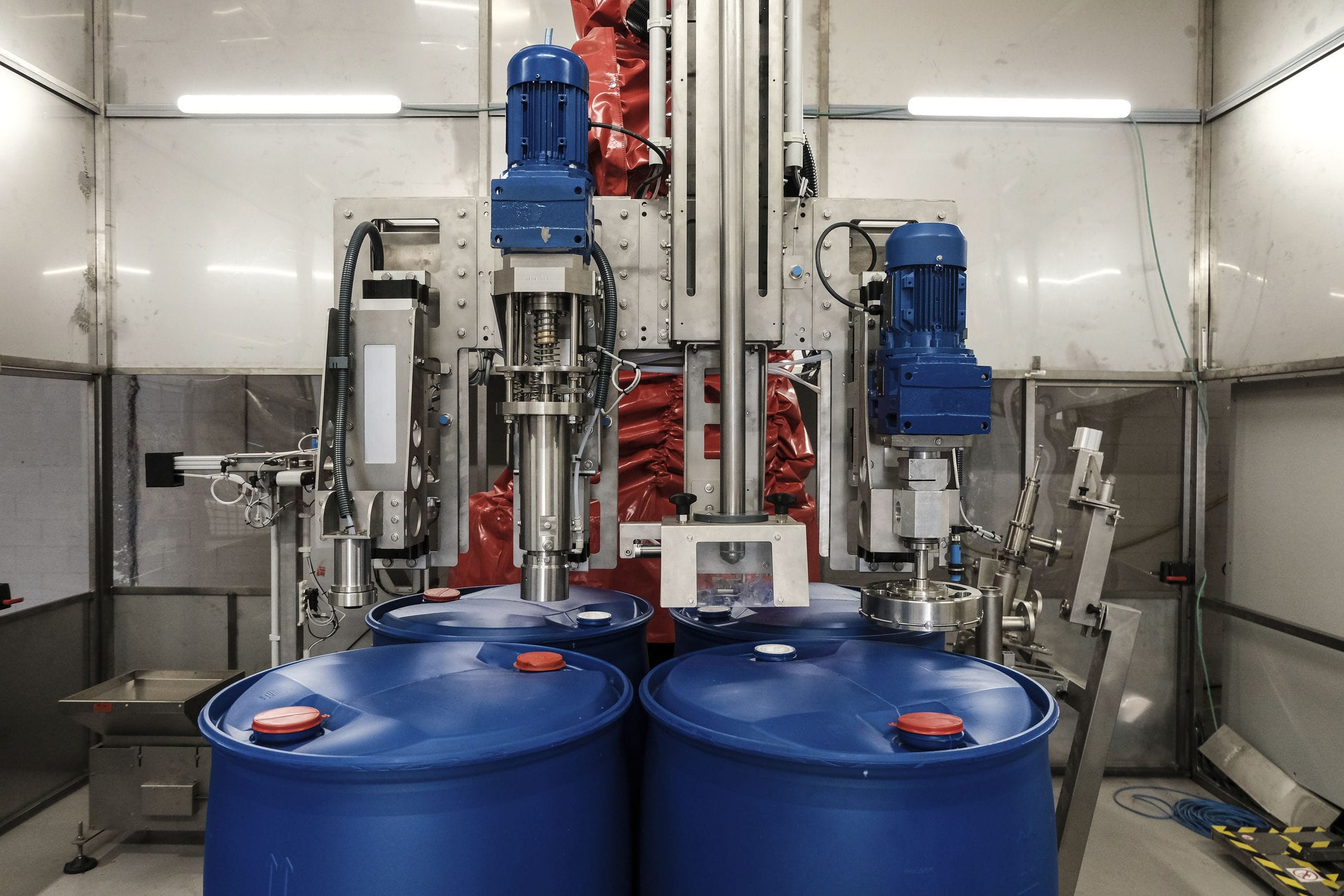
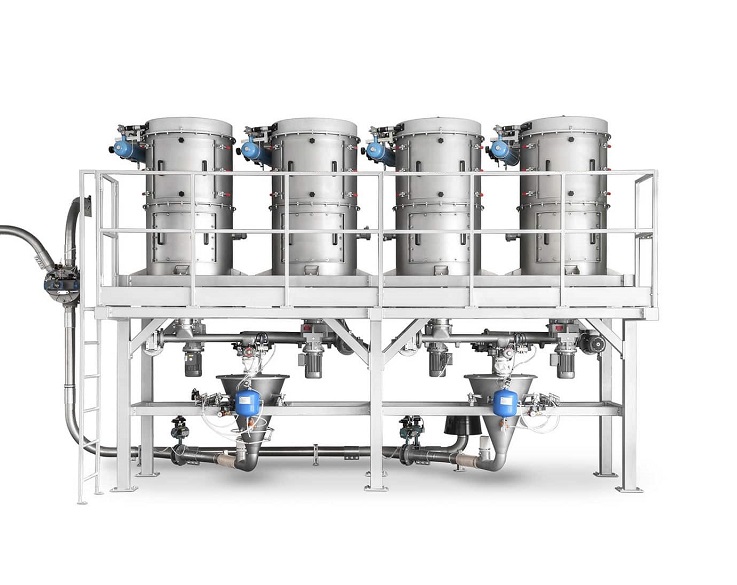
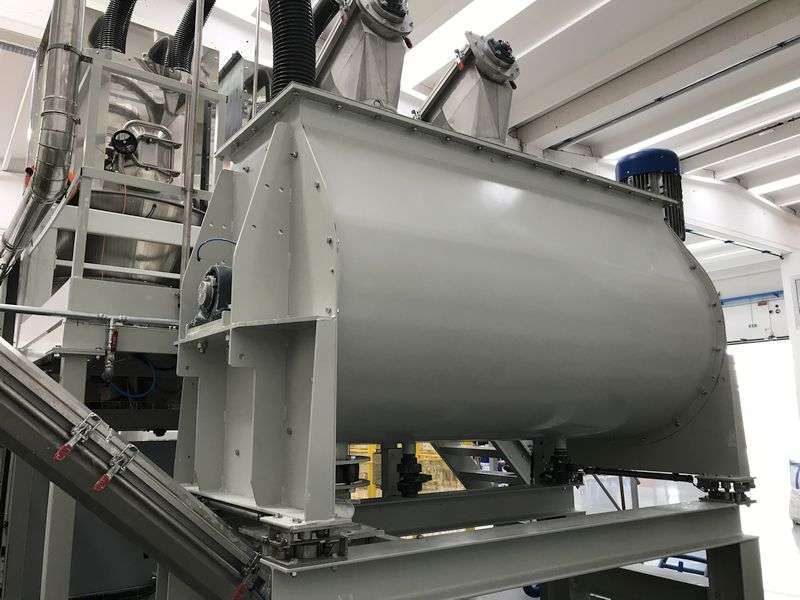
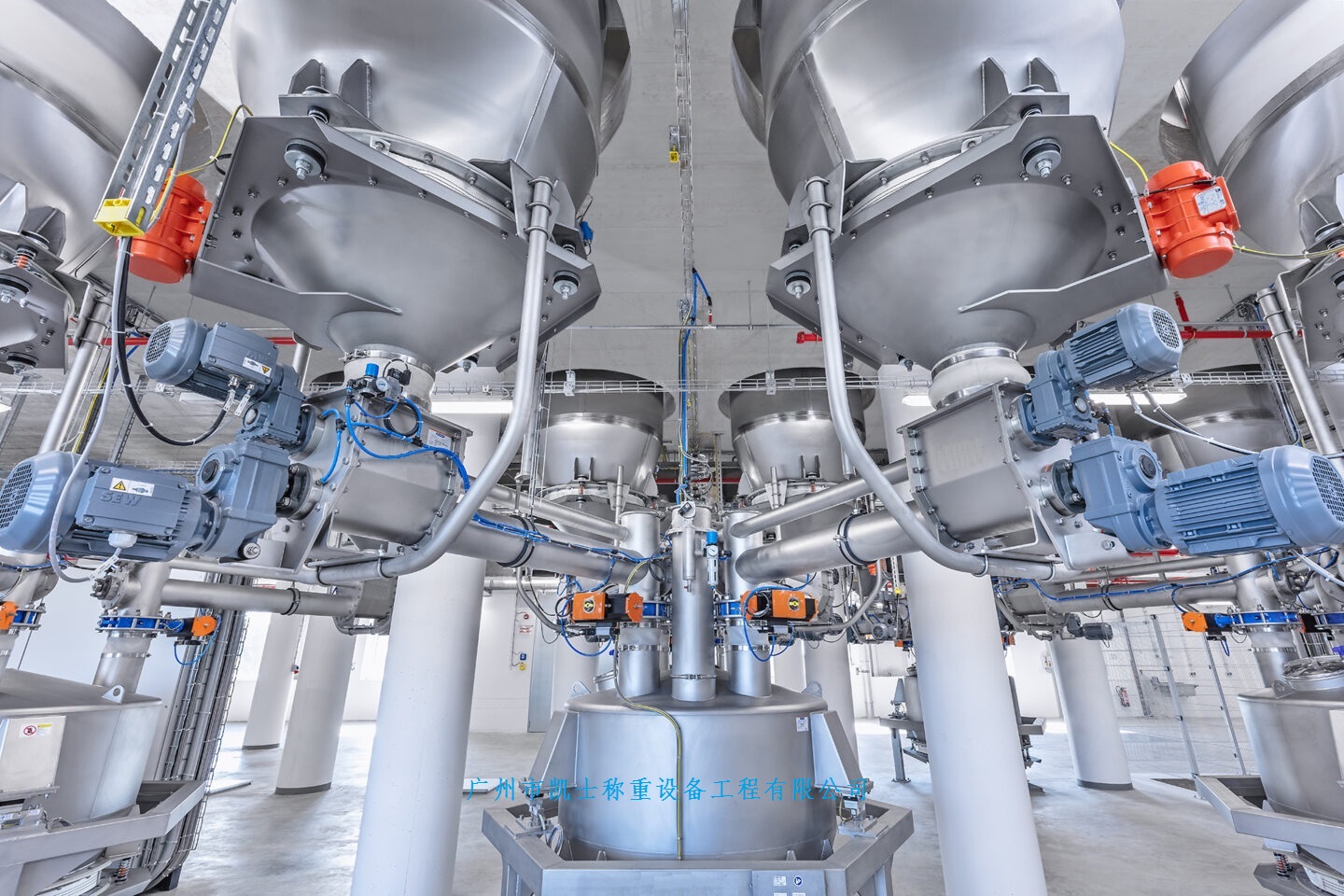
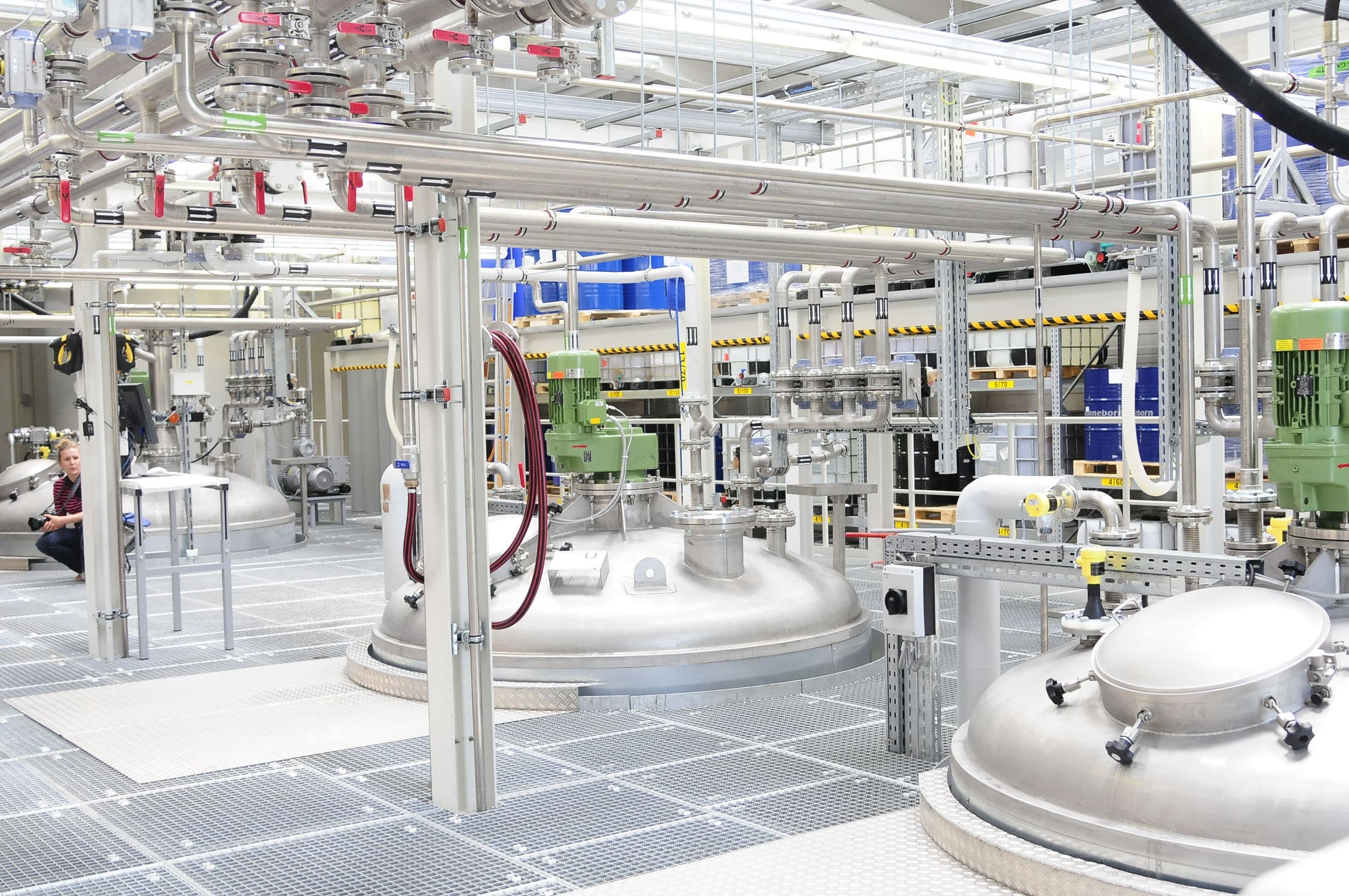
The Material Discharge weighing feeding machine, based on the principle of solid-gas two-phase flow, efficiently conveys powder materials along a closed pipeline by utilizing the static and dynamic pressure of compressed air. The powder material undergoes fluidization in the silo pump and is conveyed while fluidizing. During the batching process, the materials are first rapidly sent to the hopper scale by the Roots blower. When the feeding volume reaches 90% of the set value, it is changed to slow feeding. Once the set value is reached, the feeding is stopped. After the feeding process is completed, the system calculates the batching error and corrects the set value, preparing for the next feeding.
 020-34563445
020-34563445A Material Discharge weighing Feeding machine refers to the process of weighing different types of materials in accordance with the proportion requirements of the pre-designed raw material formula. A system that realizes the supply, weighing and discharge of materials through equipment such as silos, batching scales and Feeders. The Siemens S7-300 programmable logic controller was adopted to achieve the full automation control of the entire production process, including raw material proportioning, mixing, feeding, material distribution and discharging. The proportioning of raw materials adopts static weighing. The weighing module directly sends the weighing signal to the weighing instrument control system. The PLC reads the weighing value from the weighing module and controls the variable frequency Roots blower. During the batching process, the materials are first rapidly sent to the hopper scale by the Roots blower. When the feeding volume reaches 90% of the set value, it is changed to slow feeding. Once the set value is reached, the feeding is stopped. After the feeding process is completed, the system calculates the batching error and corrects the set value, preparing for the next feeding.
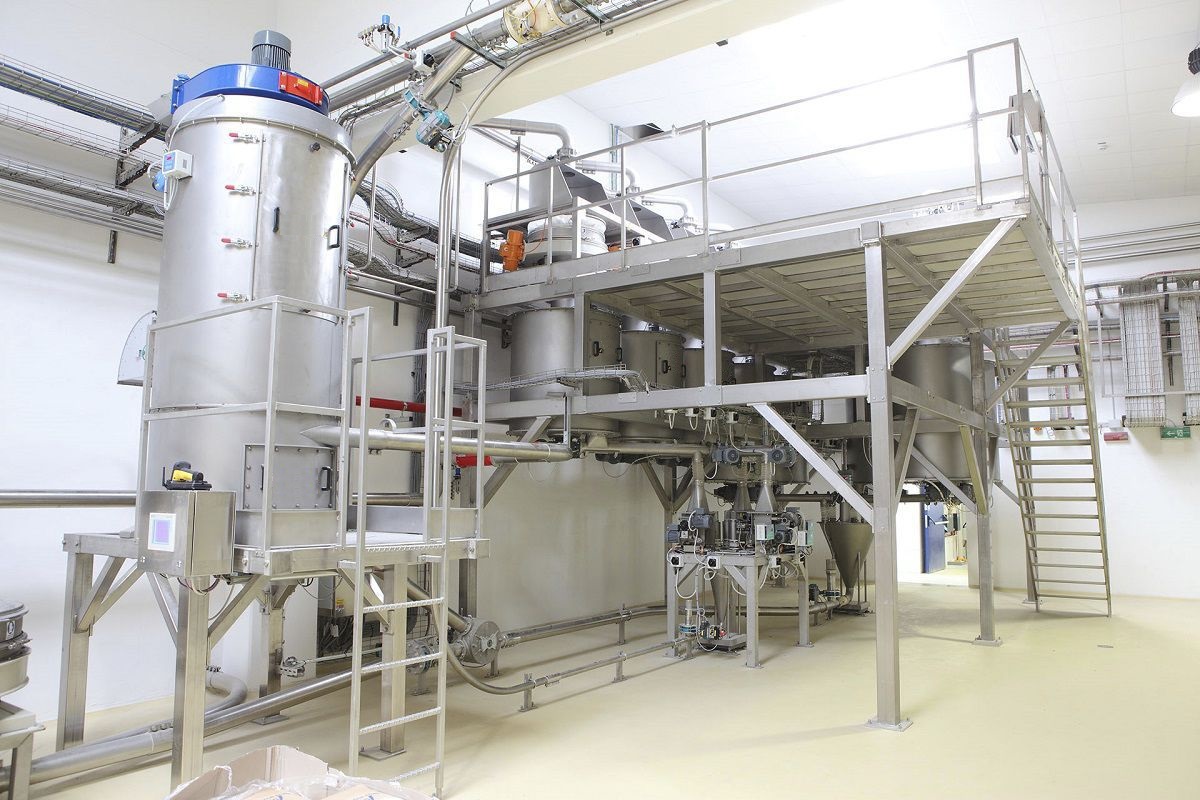
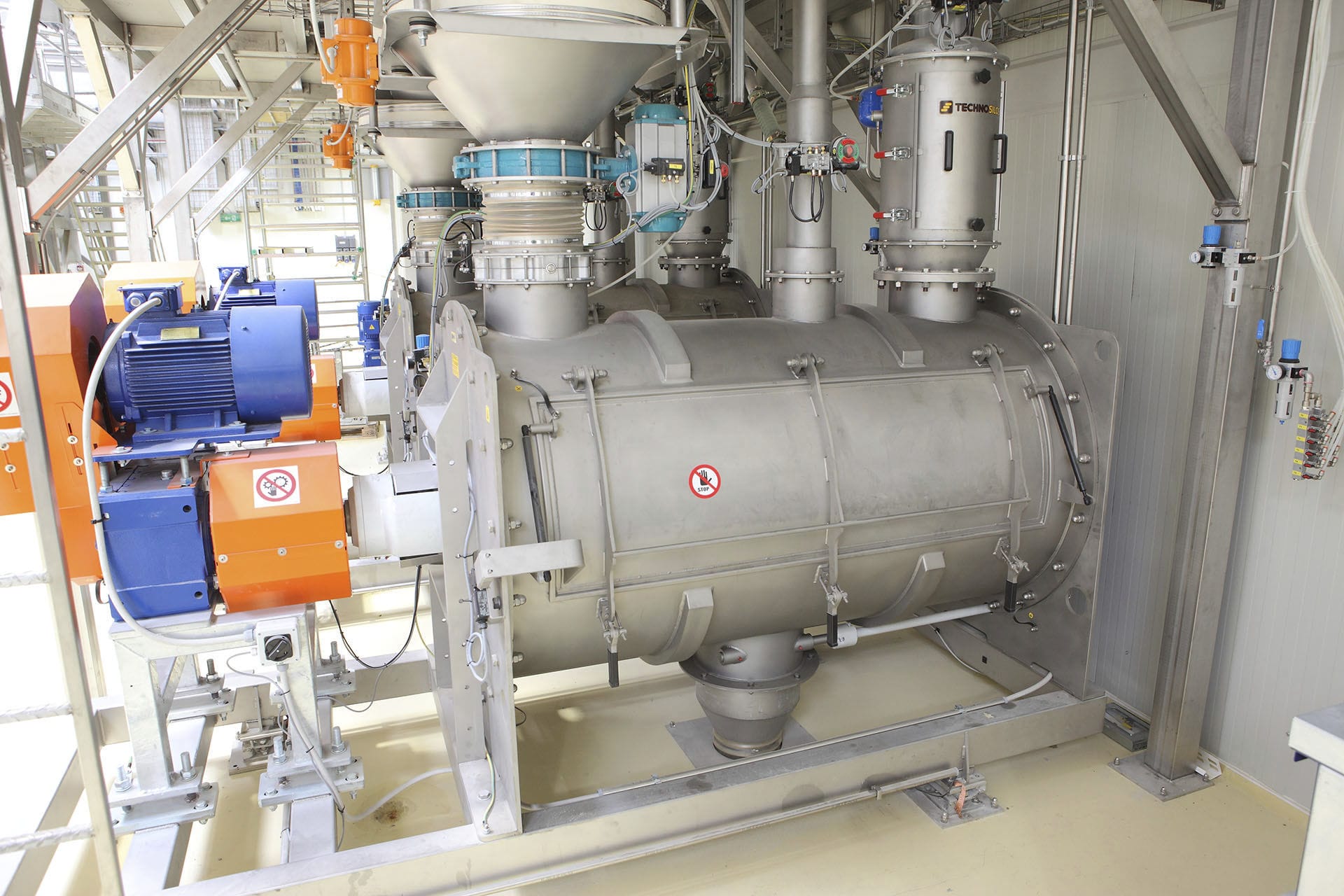
The weighing feeding machine, based on the principle of solid-gas two-phase flow, efficiently conveys powder materials along a closed pipeline by utilizing the static and dynamic pressure of compressed air. The powder material undergoes fluidization in the silo pump and is conveyed while fluidizing. The entire system consists of five parts: the air source section, the warehouse pump system section, the conveying pipeline section, the powder storage section and the control section. Among them, the conveying part is composed of corresponding specification silo pumps according to the requirements of the powder conveying volume. Each silo pump serves as a conveying unit. The powder conveyed by each silo pump constitutes one working cycle, and each cycle is divided into the following five stages.
During the feeding stage, the balance valve and the feeding valve are in the open state, while the primary air valve (the primary air serves to fluidize the powder), the tertiary air valve (the tertiary air is used to convey the powder), and the discharge valve are in the closed state. The upper part of the silo pump is connected to the powder hopper (the machine head is the middle silo), and the dust removal powder falls freely into the silo pump by gravity. When the powder level of the silo pump is too high, causing the silo pump material level gauge to send a full material signal or when the set feeding time of the system is reached, the balance valve and the feeding valve close, and the feeding stage ends.
Pressurized fluidization stage After the feeding stage is completed, the system automatically opens the primary air valve. The compressed air that has undergone dehydration and oil removal treatment passes through the flow control valve and check valve and then enters the fluidization cone at the bottom of the silo pump. After passing through the fluidization cone, it enters the silo pump to evenly surround each powder particle. At the same time, the pressure inside the silo pump rises. When the set pressurization timing is reached, the system automatically opens the discharge valve and the tertiary air valve. Then the pressurized fluidized stage comes to an end.
Conveying stage The discharge valve and the tertiary air valve are opened. At this time, the silo pump continues to take in air. The air-powder mixture enters the powder conveying pipe through the discharge valve. The powder is always in a fluidized state while entering the conveying pipeline for conveying. When the powder in the silo pump is completely conveyed, the pressure in the pipeline drops, and the pressure inside the silo pump decreases. When the pressure in the conveying pipeline drops to the set value for the end of conveying, the conveying stage ends. The primary air valve, the tertiary air valve and the discharge valve remain open and enter the purging stage.
Purging stage: The primary air valve, the tertiary air valve and the discharge valve remain open. Compressed air purses the silo pump and the powder conveying pipeline. After a certain period of time, when purging is completed, the primary air valve and the tertiary air valve are closed. After a delay of 5 seconds, the discharge valve is closed. The system then enters the feeding waiting stage.
Feeding waiting stage: All valves are in the closed position. When the waiting time is up, the balance valve and the feeding valve are opened to enter the feeding stage. At this point, the system completes one conveying cycle and automatically enters the next conveying cycle.