 2020.01.26
2020.01.26Summary:The automatic batching system controls the motors of each actuator through AC contactors, and is composed of PLC and computer to realize automatic control of the entire process.The adaptive multi-level variable-speed batching control method is adopted to realize self-tuning of batching parameters of different formulas under variable working conditions, which reduces the operational difficulty for practitioners, improves the accuracy and speed of batching, and thus improves product quality and production efficiency.
1 Composition and principle of automatic feed mill batching system
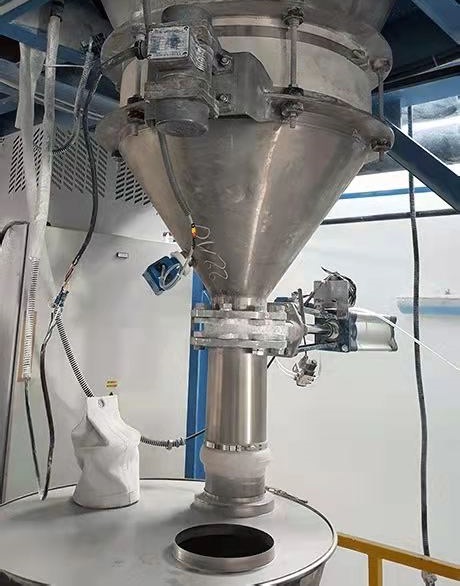
The dosage control system mainly includes the host computer, dosage controller, each component bin, variable frequency screw unloader and control valve group, dosage scale and mixer, etc. The controller as the master station communicates with the host computer and the dosage scale through Profibus bus.
The upper interface of the feeding system is written by VB, which can download the formula and set the dosage parameters through the upper computer. The dosage controller automatically selects bins according to the recipe requirements, and starts the variable frequency screw unloader and control valve under the corresponding bin, and at the same time reads the material quality of the dosage scale to detect and judge, and controls the unloader rotation speed according to the adaptive multi-stage variable speed control algorithm in order to realize the speed control of the dosage, and completes the dosage of the component if the final weighing quality is within the tolerance, and sends out an alarm for exceeding tolerance if it is larger than the tolerance, and then puts the component into the mixer after the operator has processed it. If the final weighing quality is within the tolerance range, the component will be discharged, if it is larger than the tolerance error, an alarm will be issued for over-tolerance, and the operator will put the component into the mixing machine after processing, and then start the dosing of the next component. After all components are weighed, the mixer starts to mix according to the formula setting process.
2 The realization of multi-step variable speed dosage control strategy
The accuracy and speed of the dosage process are contradictory to each other, in order to obtain the best dosage accuracy and speed, it is proposed to use multi-stage variable speed dosage control strategy, the dosage process is divided into high speed dosage, slow dosage, pulse dosage of three stages. The multistage variable speed dosage control curve contains the unloader speed curve and the material mass curve on the dosage scale, in which the parameters such as fast-slow switching point, pre-cutting point, fast-slow switching time, unloader speed, and the maximum number of dosage pulses can be set by the host computer.
Start dosage unloader speed for high speed, at this time the dosage scale on the material mass increases very quickly, to reach the fast and slow switching point mass, unloader in the fast and slow switching time to complete the fast and slow speed switching, slow dosage target time is set to t (t + t ≤ t). Arrive at the pre-cut off point mass P, the unloader stops unloading, due to the existence of the "air drop", in the stabilization time, the material quality will increase. At the end of the stabilizing time, the weighing result of the dosage scale should have three situations: one is exactly in the permissible error range, which indicates that the dosage parameters set up this time are very good, and the current parameters are saved; the second one is that the deviation is too large and exceeds the target mass positive deviation, and the dosage system has not been able to adjust the result, and it is necessary to adjust the dosage parameters; the third one is that the deviation is too large and is lower than the negative deviation of the target mass, and the dosage system enters into the impulse re-dosage stage, and the control The winch will start dosage until the dosage quality is within the tolerance of dosage error.
The unloader is mainly used for setting the parameters of pre-cut, tolerance and dosage parameters in 3 parts. The pre-cutting part is used to set the quality of the fast and slow switching point, the pre-cutting point quality and the pre-cutting maximum corrected quality, it should be noted that the pre-cutting maximum corrected quality value, this parameter is to set the adjusting range to prevent the optimization of the adjustment of the excess, the correction formula will be used in the later; tolerance setting part is used to set the quality of the positive and negative error range (i.e., the dead zone range), divided into the absolute and relative quality error two kinds of error, the actual use of the take the In practice, the smaller of the two values is taken into the operation. In addition, this part is also used to set the automatic reset error range of the system, also divided into absolute error and relative error two kinds, when the difference between the actual quality of the dosage and the target quality exceeds the dead zone partially within the automatic reset error range, the system automatically receives the quality and completes the dosage; if the difference between the actual quality of the dosage and the target quality exceeds the dead zone partially outside of the automatic reset error range the system outputs an alarm, which is confirmed and then completes the dosage, and waits for the next dosage to be made, and the system outputs an alarm. If the difference between the actual quality and the target quality exceeds the dead zone part which is not within the automatic reset error range, the system outputs an alarm and the operator confirms and finishes the dosage, and then adjusts the parameters to make the actual quality reach the set dead zone range in the next batch of dosage.
The dosage scale interface is mainly used to set up 4 parts of parameters such as dosage monitoring parameters, liquid addition parameters, dosage parameters and correction parameters. The dosage monitoring parameters are mainly used to set the delay monitoring time, monitoring cycle time and stabilizing time, etc. The delay monitoring time means that the system automatically monitors whether the unloading quality of the unloader reaches the minimum feeding quality set by the fast/slow feeding monitoring in the time period, and outputs an alarm to indicate the lack of material if the quality of the unloader does not reach the minimum feeding quality set by the fast/slow feeding monitoring. Stabilizing time is used to delay monitoring the actual quality of dosage to improve the stability of the system; Liquid adding parameter is used to set the actual calibrated liquid quality per pulse, and the system will calculate the added liquid quality according to the number of pulses collected; Dosage parameter setting part is used to set the parameters of emptying monitoring period, monitoring the quality of empty, the maximum time of empty, the quality of weighing empty, and the time of weighing empty and delayed shutdown, etc., and emptying Empty monitoring cycle means that if the unloading quality of the scale is less than the set monitoring and emptying quality within the set time, an alarm will be output to indicate the unloading failure of the scale. When the scale display quality is less than the set scale emptying quality, the system tasks the scale to be emptied and closes the scale unloading valve after the set delay time.
The parameters set at the top can be empirical values and are not necessarily optimal. After the lower PLC receives the initial given parameters, it needs to optimize the quality of the fast and slow switching point and the quality of the cut-off point in the dosage process, in order to obtain the optimal target accuracy and speed.
3 Adaptive adjustment of cutting point
The adaptive regulation system used in this paper is an adaptive system based on model reference. Model reference adaptive control system consists of a reference model, unloader (controlled object), real-time quality feedback (dosage scale feedback information) and adaptive controller, which y (t) directly represents the system hope that the output that is the target quality of each component; y (t) is the output of the unloader, that is, the actual quality of each component; the error generated between the two is e (t). The normative input (reference input) R(t) is the real-time mass of the dosage components. The multistage variable speed dosage controller controls the unloader speed and the corresponding time, i.e., u, according to the set dosage parameters (unloader speed and corresponding time) based on the deviation of the inputs and feedbacks to control the unloader output mass y(t), and if the parameter is set appropriately, y(t)/is within the set error range. Once the formula changes, the unloader speed changes, the dosage parameters then need to be adjusted. At this time, due to the initial parameters of the controlled object is uncertain (or unknown in advance), the field operator usually can only give the approximate range of dosage parameters, the initial parameters of the controller can not be adjusted very well, so the output of the controlled object y (t) and the output of the reference model y (t) generated between the error e (t) is large. When the adaptive error is induced into the adaptive regulator, after the adaptive control law operation, the multilevel continuous dosage control parameter is directly changed to produce a new control action u(d) to control the controlled object. Thus, the output of the controlled object asymptotically follows the output of the reference model until y(t) is within the set error range.
Two possible scenarios for the end of a dosage run are analyzed and given as optimized (corrected) dosage cut-off points and fast/slow dosage switching points.
If the target value (target mass) is not equal to the actual value! (actual quality), both the "fast/slow switching point" and the dosage cut-off point must be corrected. There are two types of actual situation: one is when the actual mass is small and the correction value is positive, and the other is when the actual mass is large and the correction value is negative. The quality change curve between need not be modified, so adjust and position at the same time, while up or down position. However, in order to ensure stable and orderly output, each operation only corrects 50% of the deviation. At this time the cut-off point mass; correction value = fast/slow switching point mass P, correction value = AW.
The deviation value of the target quality and the actual quality, for the maximum deviation correction value (correction factor ≤ 0.5), c: for the maximum correction value of the quality of the cut-off point, these two parameters are pre-set by the upper computer. The control optimizes the adjustment of stability and speed.
If the actual mass conforms to the tolerance range, but the measured slow transfer time (t) is not equal to the target time (t plus), this means that the cut-off point is in the right position, but the fast/slow switching point is lagging behind, and the "fast/slow switching point" must be corrected, and the value of the correction will be negative in this case. Corrections are made according to the difference between the slow dosage time and the slow dosage target time. The correction value of the weight P of the fast/slow switching point is indicated by.
4 Operation effect analysis
Multi-stage variable speed adaptive dosage system operation process recorded in a formula of a component of the automatic dosage run 16 times of data, in addition to the initial set of parameters to run the data beyond the target quality of positive deviation, the system then into the parameters of the self-tuning state, the second run to start all the data to meet the requirements of the error margins, the fifth start the data is basically stabilized in the range of the dead zone, of which 10 times the data falls within the dead zone, and the other The data of 2 times are also within the range of positive and negative tolerance, indicating that the adaptive automatic dosage system runs stably with good effect. The factors affecting the deviation between the actual quality and the target quality are random error and systematic error. Random error mainly includes the ventilation system or vibration disturbance, the component quality of different formulas, the influence of the uniform hook degree of feeding and the total quality on the scale accuracy, while systematic error mainly includes the unloading cut-off time, the length of the unloader's transferring path and so on, and the systematic error can be corrected through the program. From the data distribution range, the system operation deviation mainly comes from random error, which fully demonstrates the superiority of the operation mechanism of the dosage control system.
5 Conclusion
The system has achieved good results in the use of the process, reducing the labor intensity of workers, improving the accuracy and speed of dosage, increasing the flexibility of formula management, greatly improving production efficiency, and creating good economic benefits for the enterprise.