 2025.05.02
2025.05.02Summary:The control system of the automatic hopper scale adopts the double weighing and quantitative control realized by the relay, the feed motor feeds the preparation hopper, and the material enters into the hopper scale from the preparation hopper, at this time, the weight of the material in the hopper scale is collected by the sensor through the A/D conversion by the weighing instrument, and the weighing instrument collects the data continuously and calculates the current speed of the hopper scale feeding according to the time difference of the collected data. The pre-set value is then compared with the weight of the material in the current hopper and the time needed to continue feeding is calculated. Since the weighing instrument continuously collects data and makes judgment to calculate the new feeding speed and the time needed to feed, plus the size of the feeding port of the hopper feeding into the hopper weighing is controlled by the weighing instrument, so the accuracy of measurement can be guaranteed.
1 Introduction
Automatic quantitative hopper scale is the use of weighing instruments through the weighing module to collect data and arithmetic judgment to control the implementation of elements to achieve automatic weighing of materials and unloading control container. Currently on the market most of the single weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale is a weighing instrument only on a hopper weighing control, that is, a single feeding single unloading mode of operation. This control method has been more mature, and widely used in automatic packaging control system.
2 Single-weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale control system
2.1 The basic composition of the system
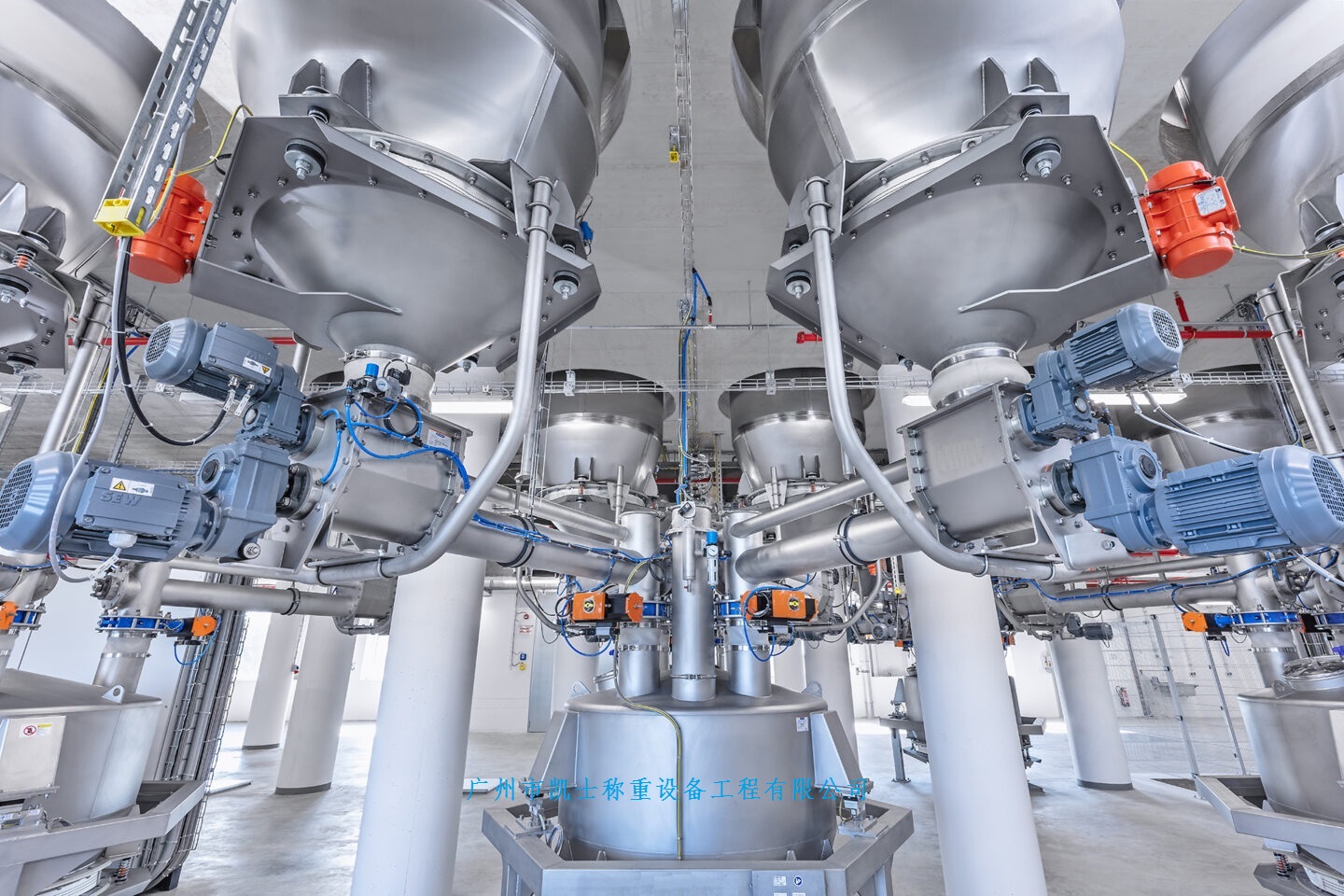
Most of the current quantitative automatic hopper scales are composed of weighing instruments, preparation hopper, hopper weigher, unloading hopper, weighing module, sealing machine, bracket and so on.
2.2 System control process
The feeding motor feeds the hopper, and the material enters into the hopper weigher from the hopper, then the weight of the material in the hopper weigher is collected by the sensor through A/D conversion by the weighing instrument, which continuously collects the data and calculates the current speed of hopper weigher according to the time difference of the collection. The pre-set value is then compared with the weight of the material in the current hopper and the time needed to continue feeding is calculated. As the weighing instrument constantly collects data and makes judgment to calculate the new feeding speed and the time needed to feed, coupled with the preparation of hopper feeding into the hopper weighing the size of the feeding port is controlled by the weighing instrument, so it can ensure the accuracy of measurement. One of the weighing instrument is to control the size of the feeding port of the hopper: at first the feeding port is the largest (big cast), when the weight of the material in the hopper weighing is close to 70%~80% of the set value (specifically set by the software part of the weighing instrument), the feeding port shrinks partly (medium cast), close to 80%~95% (specifically set by the software part of the weighing instrument), the feeding port shrinks to the smallest feeding port (small cast), finally when the hopper feeds into the hopper weighing is controlled by the weighing instrument, so it can guarantee the accuracy of the measurement. Finally, when the weight of the material in the hopper plus the weight of the falling material in the air reaches the set value, the feeding port of the hopper will be closed and the weighing will be finished. Hopper weighing unloading into the container bag can be sealed. As the hopper weighing in the unloading into the container bag at the same time not be able to feed, so each time the hopper feed to the hopper weighing pre-set values need to wait for the hopper weighing unloading is completed before you can feed again. Therefore, the working cycle is long and the efficiency is not high. And when the preparation hopper feeding to the hopper weighing the time workers also have to wait for the completion of feeding to unload into the bag. So manpower can not be fully utilized. In view of the above problems, I designed a double weighing automatic hopper scale realized by relay.
3 Relay-controlled dual-weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale
3.1 Analysis of the dual-weighing control method
There are many ways to control the double weighing, taking into account the size of the container is fixed, by reducing the unloading time to shorten the work cycle is difficult to realize, so generally used to reduce the feeding time to change the work cycle. There are generally two ways to change the feeding time: one is to improve the feed rate of the feeding mechanism; the second is to increase the number of hopper weighing. The former in the case of the selected feed motor fixed, can only increase the number of feed motor. But increase the motor will have the following problems: ① cost problems; ② installation space problems; ③ noise problems. Considering the above problems, it is not appropriate to choose more. Increase the number of hopper weighing can be a variety of ways to control the work. More commonly used is PLC programming control and microcontroller programming control. However, taking into account the PLC programmer price is slightly higher, microcontroller programming control stability is not ideal and other factors, this design mainly uses relays to control the work of the two meters, so that the two meters can work independently at the same time but also be able to communicate with each other to realize the alternating work and priority work, an effective solution to the long work cycle, the problem of large labor costs. It has better economic significance.
3.2 The design of dual-weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale realized by relays
(1) Structure of dual-weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale
Relay-controlled dual-weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale composition and single-weighing automatic hopper scale is basically the same, the difference is that the number of hopper weighing into two, weighing control device has two internal weighing instruments, the internal structure of the hopper and weighing instrument control circuit have also changed.
(2) Double weighing working process
The material is sent to the preparation hopper by the material supplying organization, and then fed to the two hoppers by the preparation hopper. Whoever finishes the quantitative weighing first in the two hoppers will unload the material to the container bag first, and the other hopper waits until the unloading of the first one finishes, and then unloads the material again. If dosing is completed at the same time, hopper weigher 1 will discharge first. In a hopper weighing unloading, if another hopper weighing has not been completed quantitatively, the preparation hopper continues to feed into the hopper weighing until the completion of the quantitative, the corresponding outlet before sealing. The whole weighing, unloading, mutual coordination process and clip bags, loose bags are controlled by the weighing control device.
3.3 Relay to realize the working principle of double weighing quantitative control
The switching output of the weighing instrument adopts the off-electrical isolation mode, and the switching input of the instrument is valid low level: the output is the open collector transistor output, which can directly drive the DC relay or small DC load. In order to enable the two weighing instruments to communicate with each other and work alternately, the design of the fixed-value signal control, divided into four cases for discussion: ① When the first weighing instrument fixed-value signal first, J1 coil is energized, J1 normally open contact closure, which is equivalent to a switch transistor T1 is turned on. Coil KA1 will be energized, KA1 normally open contact closure, unloading solenoid valve 1 energized and start unloading. In the unloading solenoid valve 1 unloading process, if the second weighing instrument to the fixed value signal, J2 coil energized, but at this time J1 energized high level signal through the optocoupler U1 after the low level, and then with the J2 energized high level signal through the logic and the gate is still low, then the transistor T2 is still equivalent to the work of a switch on the off state. So KA2 coil can not be energized, unloading solenoid valve 2 can not unload. The realization of the solenoid valve 1 unloading and solenoid valve 2 can not be unloaded at the same time function. ② When the second weighing instrument fixed value signal first, J2 coil is energized, J2 normally open contact closure, and the input terminal 1 of gate U2 is high level at this time. As J1 coil is not energized, so with the input terminal 2 of the gate U2 is also a high level, the output terminal 3 is a high level. At this time, transistor T2 is equivalent to a switch on. Relay KA2 coil is energized, KA2 normally open contact closure, unloading solenoid valve 2 on and start unloading. KA2 normally closed contact disconnect, cut off the unloading solenoid valve 1 on the circuit. The realization of the solenoid valve 2 unloading and solenoid valve 1 can not be unloaded at the same time function. From ① and ② analysis, unloading solenoid valve 1 and unloading solenoid valve 2 connection can be realized interlock. This also realizes the function of double feeding and single unloading, i.e. double weighing control. ③ When the fixed value signal of the two weighing instruments arrives at the same time, transistor T1 works in the on state of the switch. Relay KA1 coil is energized, normally open contact is closed, unloading solenoid valve 1 is energized and starts unloading. Since the input 2 of the gate U2 is low level after the relay J1 coil is energized, it remains low level after passing through the gate, and the transistor T2 works in the switch off state. The unloading solenoid valve 2 is not energized and unloading is not possible. Thus, the function of unloading is realized that the weighing instrument 1 has priority when the fixed value signals of two weighing instruments arrive at the same time. When the fixed value signals of both weighing instruments do not arrive, both solenoid valves do not unload. When one unloading is finished, the unloading solenoid valve will put the
4 Conclusion
The circuit is designed in combination with the weighing instrument. Without changing the software of the controller, the structure of the single-weighing quantitative automatic hopper scale is changed, and some hardware circuits are added at the same time, which overcomes the problems of long working cycle, low efficiency, and human resources cannot be fully utilized in the single-feeding and single-unloading. Reasonable structural changes, with simple circuit control, effectively realize the double weighing in one. The main advantages of this product are cheap price, high working efficiency, good performance, very suitable for the measurement and control of different materials that are often changed.